Question
Question: What is the geometry of complexes having hybridization \( s{p^3} \) and \( ds{p^2} \) . Give an exam...
What is the geometry of complexes having hybridization sp3 and dsp2 . Give an example of each.
Solution
Hybridization is the mixing of atomic orbitals with the same energy to form a new degenerate orbital. The orbital thus formed is called the hybrid orbital. Hybrid orbitals possess different geometry and energy than that of the individual atomic orbitals. sp,sp2,sp3,sp3d2,d2sp etc. are examples of few hybridised orbitals.
Complete answer:
Atomic orbitals of equal energy mix to form a hybrid orbital. Both half-filled and completely filled orbitals can take part in hybridisation. The number hybrid orbitals will be equal to the number of atomic orbitals that took part in mixing.
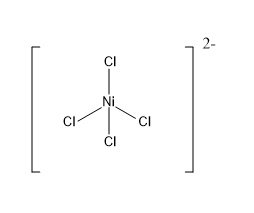
sp3 hybridization: It is formed by the mixing of one s orbital and three p orbitals of the same shell of an atom that are equal in energy. Mixing of these orbitals give 4 equivalent hybrid orbitals with sp3 hybridization. An sp3 hybridised orbital contains 25% s character and 75% p character. The geometry of complexes possessing sp3 hybridization will be tetrahedral. The four atoms bound to the central atom will be directed towards the four corners of the tetrahedron. The bond angle will be 109∘28′ .
Example: [Ni(Cl)4]2− .
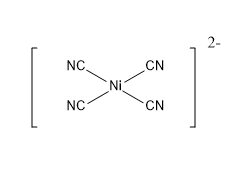
dsp2 hybridization: Mixing of dx2−y2 orbital, one s orbital and two p orbitals of equivalent energies gives four equivalent dsp2 (+2) hybridised orbitals. An dsp2 hybridized orbital contains 25% d character, 25% s character and 50% p character. The geometry of a dsp2 hybridised complex is square planar. The bond angle between the ligand-central atom-ligand will be 90∘ .
Example : [Ni(CN)4]2−
Note:
Though the central atom and its oxidation state (+2) are the same in both the complexes, the difference in the geometry of the complex is due to the nature of ligands. Strong ligands will form dsp2 complexes, while weak ligands will form sp3 hybridised complexes.
It should be noted that molecular orbitals and hybrid orbitals are not the same. Molecular orbitals are formed by the interaction of different atomic orbitals while hybrid orbitals are formed by the mixing of atomic orbitals of the same atom.
