Question
Question: What is the formula for copper \( \left( {II} \right) \) carbonate?...
What is the formula for copper (II) carbonate?
Solution
Copper (II) carbonate is a chemical compound which is an ionic solid at ambient temperatures. It consists of copper (II) cations Cu2+ and carbonate anions CO32− . Copper (II) carbonate is a grey coloured ionic solid. It is a non-flammable compound.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Copper (II) carbonate is rarely confronted because it is very strenuous to prepare and reacts with water moisture of the air very rapidly. The terms “Copper carbonate”, “Copper (II) carbonate” and “cupric carbonate” are referring to the basic copper carbonate.
The structure of Copper (II) carbonate is shown in the figure below:
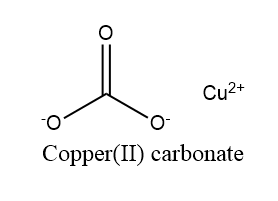
The Copper (II) carbonate reacts very rapidly with water and air thus it is practically a monotonous process to prepare.
Copper (II) carbonate can be yield by the reaction of copper (II) sulphate CuSO4 and sodium carbonate Na2CO3 in ambient condition, produce instead a basic carbonate and CO2 , because of the great affinity of the Cu2+ ion for the hydroxide anion OH− .
W.F.T Pistorius in 1960 ; asserted synthesis by heating basic copper carbonate at 180∘C in the atmosphere of carbon dioxide and water for 36 hours. The proportions of the products were malachite Cu2CO3(OH)2 , but small amount of rhombohedral substance was also formed, claimed CuCO3 . But this synthesis was apparently not reproduced.
The chemical formula of Copper (II) carbonate is CuCO3 which contain Copper (II) cation Cu2+ and carbonate anion CO32− .
Note:
The stability of dry carbon (II) carbonate depends upon the partial pressure of carbon dioxide CO2 . It is stable for months in dry air however slowly decomposes into copper (II) oxide and carbon dioxide.
