Question
Question: What is the end product (B) in the following reaction sequence?  in the following reaction sequence?
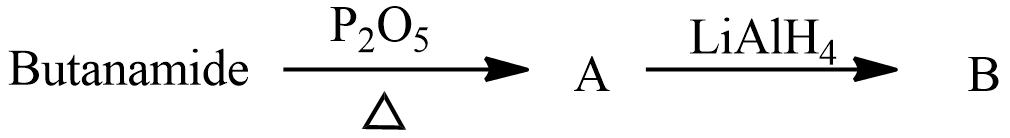
(A) n−butylamine
(B) n−propylcyanide
(C) propylisocyanide
(D) n−propylamine
Solution
Above reactions suggest that butanamide CH3CH2CH2CONH2 reacts with Phosphorus pentoxide P2O5 to give product A and when Product A is treated with Lithium Aluminium hydride LiAlH4 it gives a product B. Phosphorus pentoxide is used for dehydration reaction to convert amides into nitriles. Lithium Aluminum hydride is a reducing agent used to convert cyanides into amines.
Complete answer:
Phosphorus pentoxide is a dehydrating agent, it is used for the conversion of nitriles from primary amides. Since butanamide is a primary amide, it will undergo dehydration to form cyanide and water the reaction taking place will be:
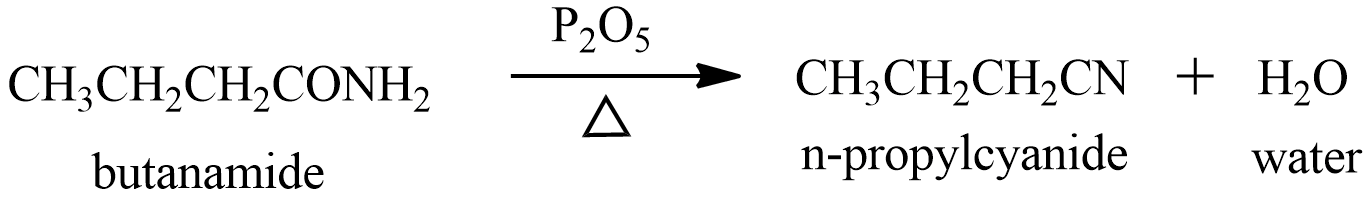
From the reaction we can see the product formed is n−propylcyanide . According to the question the n−propylcyanide is the product A.
Now, product A or n−propylcyanide is treated with Lithium Aluminum hydride which is a reducing agent used to convert cyanides or nitriles into amines to get product B, the reaction taking place will be:

From the reaction we can see the product formed is n−butylamine . According to the question the n−butylamine must be the product B.
So, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note:
Phosphorus pentoxide is a very good dehydrating agent it is used in different areas as a part of Onodera reagent which is used for the oxidation of alcohols, used for converting some mineral acids into anhydrides. Lithium Aluminum hydride is a good reducing agent it is used to reduce polar bonds. It has many uses: it is used to convert aldehyde and ketone to primary and secondary alcohols respectively, carboxylic acids to primary alcohols, amides and nitrile to amines.
