Question
Question: What is the electronic configuration of Nitrogen monoxide?...
What is the electronic configuration of Nitrogen monoxide?
Solution
Hint : In molecular orbital theory, the bonding orbital is used to explain the favorable relations between two or more atoms' atomic orbitals in a molecule. Electrons are depicted as moving in waves in the MO principle.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
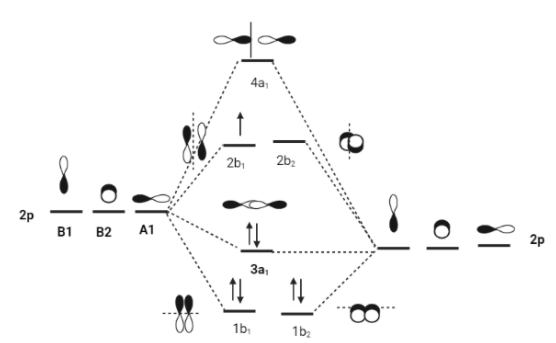
Steps involved in molecular orbital theory are: Considering electrons to be delocalized in the molecule, integrating atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ,σ∗,π,π∗), producing bonding and antibonding relationships depending on which orbitals are filled, and predicting electron structure in molecules.
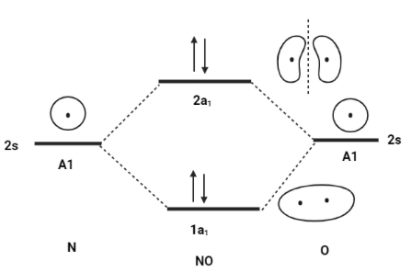
σ2sBonding MO is represented by 1a1.
σ∗2sAntibonding MO is represented by 2a1.
π2PxBonding MO is represented by 1b1.
π2PyBonding MO is represented by 1b2.
σ2PxBonding MO is represented by 3a1.
π∗2PxAntibonding MO is represented by 2b1.
π∗2PyAntibonding MO is represented by 2b2.
σ2PxAntibonding MO is represented by 4a1.
Additionally, the 2s−2s overlap is the same concept as the 1s−1s overlap. As a result, the molecular electron structure will be written in the same way as the atomic version, but with molecular orbitals instead of atomic orbitals.
Hence, we get,
(σ1s)2(σ1s∗)2(σ2s)2(σ2s∗)2(π2px)2(π2py)2(σ2px)2(π2px∗)1
Note :
The valence-bond principle fails to understand exactly how many compounds, such as resonance-stabilized molecules, contain two or more identical bonds whose bond orders lie between those of a single bond and those of a double bond. This is where the molecular orbital concept proved to be more strong than the valence-bond theory
