Question
Question: What is the effect of p\({ CO }_{ 2 }\) on oxygen transport?...
What is the effect of pCO2 on oxygen transport?
Solution
The partial pressure of CO2 (pCO2) and the partial pressure of O2 (pO2) and the relative difference between their values is what decides the rate and direction of diffusion at the different parts of our body.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Oxygen is transported in the blood by hemoglobin which forms a complex known as oxyhemoglobin while doing so. The binding of oxygen to this hemoglobin depends on a number of factors such as pCO2, pO2, and H+ concentration.
If pCO2 is high, H+ concentration is high and pO2 is low along with high temperature, then in such conditions, the dissociation of oxyhemoglobin is favored. This means that oxygen will be used for cellular respiration instead of being transported.
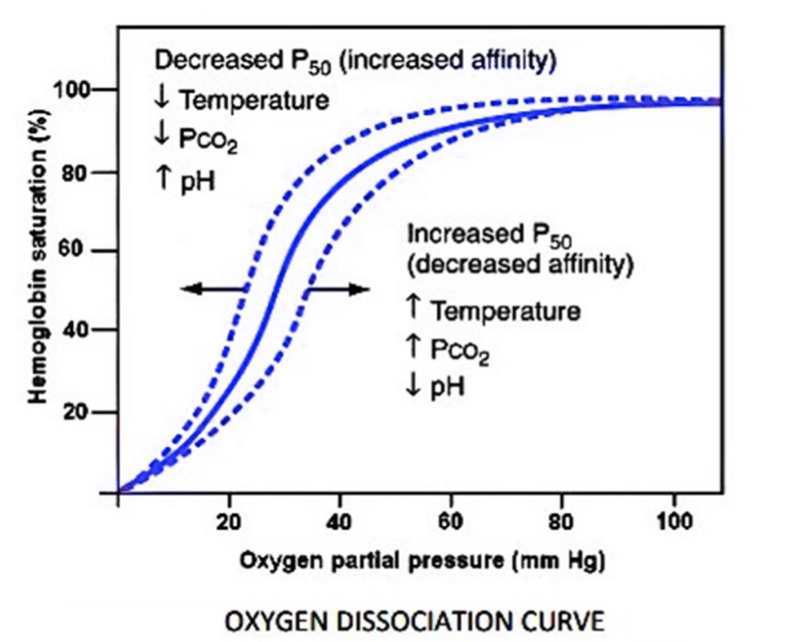
If pCO2 is low, H+ concentration is low and pO2 is high along with low temperature, such conditions favor the formation of oxyhemoglobin and thus oxygen is likely to be transported.
Additional information: Regulation of oxygen transport is also done via the neural system.
Respiratory rhythm center: This is a specialized region present in the medulla region of the brain which can detect CO2 and H+ concentration increase in the blood and thus make changes to reduce them.
Pneumotaxic center: Pneumotaxic region helps in the functioning of the respiratory rhythm organ by signaling it in the case of high CO2 and H+ concentration.
There are not many roles of the O2 in the regulation of its transport.
Note:
- 97% of oxygen is transported in the blood in the form of oxyhemoglobin. The other 3% is transported as a dissolved gas in the plasma.
- 20%−25% of CO2 is transported by hemoglobin and 70% of it is transported as bicarbonate ions. And the remaining 7% is transported as a dissolved gas in the plasma.
- The formation of bicarbonate ions from CO2 and H2O is catalyzed by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase.
