Question
Question: What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms in organization of their cell...
What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms in organization of their cells?
Solution
Unicellular organisms have a single cell that performs all the work required. These organisms are far simpler. Multicellular organisms have many cells and they are more complex in nature.
Complete answer: The body is composed of a single cell in unicellular species that can undergo cell division to regenerate. To perform different functions, the cell has numerous organelles. Being a single cell, it is exposed to all sides of the environment. There is no labour separation. Due to a small surface to volume ratio, the cell body cannot achieve a large size, and injury to the cell can cause hazards.
In multicellular species, multiple cells make up the body. Such cells are designed to perform various functions. Cells are grouped into tissues and are a community of cells within an organism that has a similar role. To perform a particular purpose, different tissues come together to form an organ. The more complex species have organ systems. They are, for example, mammals, trees, etc.
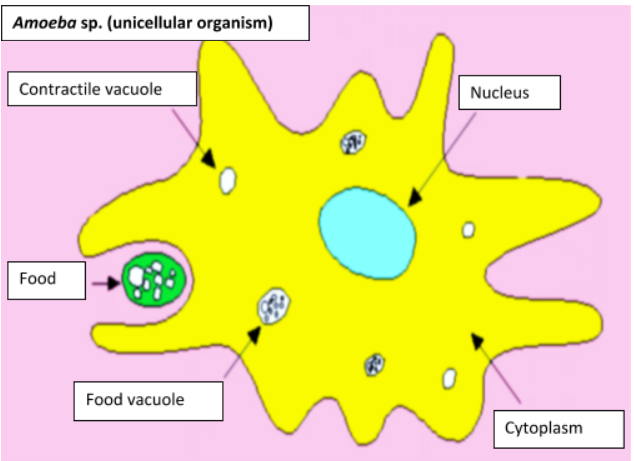
Note: A group of organs that work together to perform complex, linked tasks, concentrating each organ on a part of a mission, is called an organ system. Thus, in multicellular species, the division of labour is shown. For example, in the human digestive system, food is chewed in the mouth, crushed in the stomach, broken down by enzymes in pancreatic and gastric juices into macromolecules and consumed by the small intestines.
