Question
Question: What is the difference between structural isomers, geometrical isomers and enantiomers?...
What is the difference between structural isomers, geometrical isomers and enantiomers?
Solution
Isomers: The compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formula are known as isomers. The isomers are further divided into two types i.e., structural isomers and stereoisomers based on the type of change in the structural formula of the compound.
Complete answer: Isomers are mainly categorized into two types:
1.Structural Isomers
2.Stereoisomers
Structural isomers: The compounds having the same molecular formula but structural formula differ in the bonding of atoms present in the compound.
There are different types of structural isomers:
1.Chain isomers: Compounds having the same molecular formula but differ in the branching of carbon atoms are known as chain isomers.
Example: n-butane ⇒CH3CH2CH2CH3
Iso-butane ⇒CH3CH(CH3)CH3
In n-butane there is no branching of the chain whereas in iso-butane, a methyl group is attached to the second carbon atom. Hence these are chain isomers to each other.
2.Position isomers: Compounds having the same molecular formula but differ in the position of functional groups are known as position isomers.
Example: 1− chlorobutane ⇒CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl
2− chlorobutane ⇒CH3CH(Cl)CH2CH3
In 1− chlorobutane, chlorine is present at the first position whereas in 2− chlorobutane, chlorine is present at the second position in the carbon chain. Hence these are positional isomers to each other.
3.Functional isomers: Compounds having the same molecular formula but different functional groups are known as functional isomers.
Example: Propanone ⇒CH3COCH3
Propanal ⇒CH3CH2CHO
In Propanone, ketone is present as a functional group whereas in Propanal, an aldehydic group is present. Hence these are functional isomers to each other.
Stereoisomers: The compounds having the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms in three-dimensional space are known as stereoisomers. Geometrical isomers and enantiomers are types of stereoisomers.
Geometrical isomers: It is also known as cis-trans isomer. It generally arises in the alkenes in which each unsaturated alkene consists of two different functional groups. It is further divided into two types:
1.Cis-isomer: When the same groups are present in same side of alkene then it is known as cis isomer.
Example: cis-2-butene
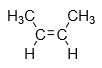
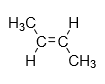
2.Trans-isomer: When the same groups are present on different side of alkene then it is known as cis isomer.
Example: trans-2-butene
Enantiomers: These are the chiral compounds which are mirror images of each other.
Example: 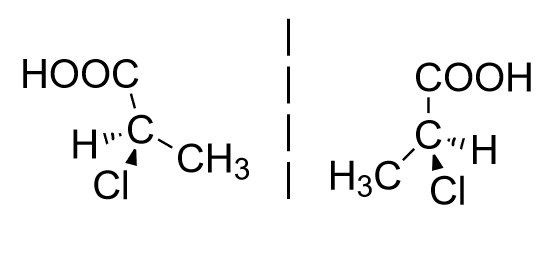
Note:
It is mandatory for a compound to be chiral to form enantiomers. Only compounds with chiral carbon can be classified as enantiomers. Enantiomers are further categorized as R-conformation and S-conformation which is done according to CIP priority rules.
