Question
Question: What is the difference between Carbocation and Carbanion?...
What is the difference between Carbocation and Carbanion?
Solution
Carbocation and Carbanion are two terms that are frequently used in organic chemistry. These are organic chemical species bearing an electrical charge on a carbon atom. These are found as intermediates of some reactions.
Complete answer:
Carbocation is generally defined as an ion in which the central carbon atom is positively charged. A carbocation can have one or more positive charges in its central atom, it is normally unstable because due to the loss of electrons, the p orbitals are free due to loss of electrons. Carbocations are paramagnetic due to incomplete electron pairing. It shows sp2 hybridization.
Types of Carbocations:
There are four types of carbocation:
1. Methyl Carbocation- These carbocation contain a positively charged carbon atom that is not attached to any other carbon atoms.
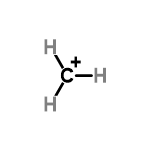
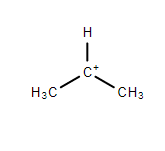
2. Primary Carbocation- The positively charged carbon atom in the carbocation is connected to another carbon atom through a covalent bond. This carbocation is stable than methyl carbocation but is less stable than other Carbocations.
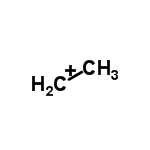
3. Secondary Carbocation- The positively charged carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms. These Carbocations are more stable than primary Carbocations.
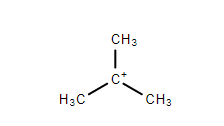
4. Tertiary Carbocation- The positively charged carbon atom is attached to three other carbon atoms. This form is very stable.
Carbanion is an ion that contains a negatively charged carbon atom. In this a carbon atom bearing negative charge is sp3 hybridized and the geometry is pyramidal. Carbanion is diamagnetic due to completion of electron pairing.
There are four types of carbanion:
1. Methyl Carbanion- The negatively charged carbon atom is not bonded to any other carbon atom.
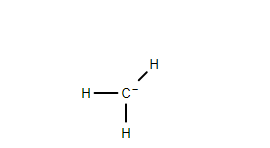
2. Primary Carbanion- Here the negatively charged carbon atom in the carbanion is connected to another carbon atom through a covalent bond.
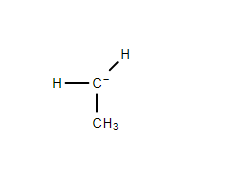
3. Secondary Carbanion- The negatively charged carbon atom is bonded to two other carbon atoms.
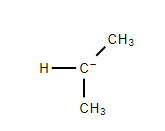
4. Tertiary Carbanion- The negatively charged carbon atom is attached to three other carbon atoms.
Difference between Carbocation and Carbanion:
| Serial number | Carbocation | Carbanion |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | A carbocation is an ion having a central carbon atom which is positively charged | A carbanion is an ion having a central carbon atom which is negatively charged. |
| 2. | The carbon atom is sp2 hybridized | The carbon atom is sp3 hybridized |
| 3. | Geometry is trigonal planar | Geometry is Pyramidal |
| 4. | Carbocation is paramagnetic | Carbanion is Diamagnetic |
| 5. | It act as an electrophile | It act as an nucleophile |
| 6. | It is more stabilized due to the presence of three donor methyl groups which donate electrons and therefore greatly stabilize the positive charge. | It is less stabilized. |
| 7. | An electron deficient specie | An electron rich species. |
| 8. | There are 6 electron in the outermost shell | There are 8 electrons in the outermost shell |
| 9. | It accepts an electron pair from a nucleophile to produce a covalent bond. | Normally donate an electron pair to an electrophile to produce a covalent bond. |
Note:
In various chemical reactions, the carbocation performs as an electrophile; conversely in many chemical reactions, the carbanion acts as a nucleophile.
Carbocation is formed if the organic molecule has a good leaving group, it can leave the molecule through ionization. The ionization gives the bonding electron pairs to the leaving group, resulting in a positive charge on the carbon atom. (CH3)2CH−∙∙O∙∙H→(CH3)2CH++∙∙∙∙O∙∙H− .
