Question
Question: What is the decreasing order of the stability of the given ions? \({\rm I})\) \({H_3}C - H{C^ + } ...
What is the decreasing order of the stability of the given ions?
I) H3C−HC+−CH3
II) H3C−HC+−O−CH3
III) 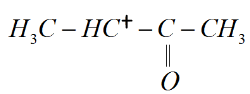
1. I>II>III
2. II>III>I
3. III>I>II
4. II>I>III
Solution
Check for electron donating/withdrawing groups, lone pair atoms, +I effect groups around the carbonium ion. These types of groups contribute to the high or low stability of the carbonium ion by either donating or withdrawing electrons/electron clouds around the cation.
Complete step-by-step answer: Let us discuss the stability of each carbonim ion:
I) In this molecule, the carbonium ion is attached to two CH3 groups. These two groups are +I effect i.e. positive inductive effect groups. These groups contribute electron clouds to the carbonium ion making it moderately stable.
II) In this molecule, the carbonium ion is attached to one CH3 group and has a single bond with an Oxygen atom. This Oxygen atom consists of a lone pair and hence it becomes a donating group. This creates resonance between both the Carbon and Oxygen atoms contributing to the higher stability of the carbonium ion.
III) This molecule consists of a ketone group attached to the carbonium ion which is an electron withdrawing group. This makes the carbonium ion highly unstable.
Additional information: The stability of a carbocation/carbonium ion depends on the neighboring carbon atoms attached to it. Tertiary carbocation has the highest stability followed by secondary followed by primary. This order completely changes when there are other functional groups attached to the carbocation.
Therefore, the correct order of the stability of the ions is II>I>III i.e. option 4.
Note: It is important to check for any resonance occurrence when it comes to groups with lone pairs as this resonance can completely change the order of stability of the carbonium ion. If there is a molecule that has resonance then that carbocation will have the highest stability.
