Question
Question: What is the cosecant and cotangent of \[\dfrac{\pi }{3}\] ?...
What is the cosecant and cotangent of 3π ?
Solution
Hint : Here in this question, we have to find the value of trigonometric ratio cosecant and cotangent at an angle of 3π . This can be found by using the equilateral triangle and Pythagora's identity. And later by using the definition of cosecant and cotangent ratios of trigonometric on simplification, we get the required solution.
Complete step by step solution:
to 60∘ i.e., 3π=60∘ .
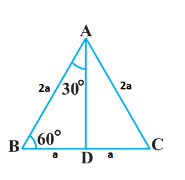
Consider an equilateral triangle ABC. Since each angle in an equilateral triangle is 60°, therefore, ∣!A=∣!B=∣!C=60∘
Draw the perpendicular AD from A to the side BC.
∴ΔABD≅ΔACD
ΔABD is a right triangle, right-angled at D with ∣!BAD=30∘ and ∣!ABD=60∘
For finding the trigonometric ratios, we need to know the lengths of the sides of the triangle. So, let us suppose that AB=AC=BC=2a . Then,
⇒BD=21BC
⇒BD=21BC
⇒BD=21⋅2a
⇒BD=a
Now, the height of the ΔABC is AD then by Pythagoras theorem i.e., AB2=AD2+BD2 , then
⇒AD2=AB2−BD2
⇒AD2=(2a)2−(a)2
⇒AD2=4a2−a2
⇒AD2=3a2
⇒AD=3a2
On simplification, we get
⇒AD=3a
In ΔABD , for the angle ∣!A=60∘=3π , side AD is a opposite side, AB is hypotenuse and BD acts as a adjacent side, then
Now, use the definition of trigonometric ratios
Definition of sine ratio at ∣!A=60∘=3π is:
sin(3π)=HypotenuseOpposite
⇒sin(3π)=ABAD
⇒sin(3π)=2a3a
On simplification, we get
⇒sin(3π)=23
Definition of cosine ratio at ∣!A=60∘=3π is:
cos(3π)=HypotenuseAdjacent
⇒cos(3π)=ABBD
⇒cos(3π)=2aa
On simplification, we get
⇒cos(3π)=21
As we know, by the definition of trigonometric ratios cosecant is a reciprocal of sine.
Cosecant ratio at ∣!A=60∘=3π is:
csc(3π)=sin(3π)1
On substituting value of sin(3π) , we have
⇒csc(3π)=231
On simplification, we get
⇒csc(3π)=32
Again, by the definition we know, cotangent is the ratio between the cosine and sine, then
cotangent ratio at ∣!A=60∘=3π is:
On substituting value of cos(3π) and sin(3π) , we have
⇒cot(3π)=sin(3π)cos(3π)
⇒cot(3π)=2321
⇒cot(3π)=21×32
On simplification, we get
⇒cot(3π)=31
Hence, the value of csc(3π)=32 and cot(3π)=31
So, the correct answer is “ csc(3π)=32 and cot(3π)=31 ”.
Note : When solving these type of questions, first we have to know the definition of six trigonometric ratios i.e., sine, cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant and cotangent and know the property of equilateral triangle i.e., all sides and angles of equilateral triangle is equal and know the formula of Pythagoras theorem i.e., hyp2=adj2+opp2 .
