Question
Question: What is the basicity of orthophosphoric acid? (A) One (B) Two (C) Three (D) Four...
What is the basicity of orthophosphoric acid?
(A) One
(B) Two
(C) Three
(D) Four
Solution
Molecular formula of orthophosphoric acid is H3PO3. Basicity of the acid is the number of protons the acid can give upon dissolution in an aqueous medium. Generally, the acidic protons are protons of the –OH group.
Complete step by step solution:
First of all, we need to know the structure of orthophosphoric acid in order to find its basicity.
-The word ortho in orthophosphoric acids indicates that this acid is having a maximum number of hydroxyl groups amongst other isomeric forms.
-The word Phosphorus in orthophosphoric acid also indicates the oxidation state of the phosphorus atom which is +3. That means P is in +3 oxidation state and there are a maximum number of hydroxyl groups present in the structure. So, we can give the following structures.
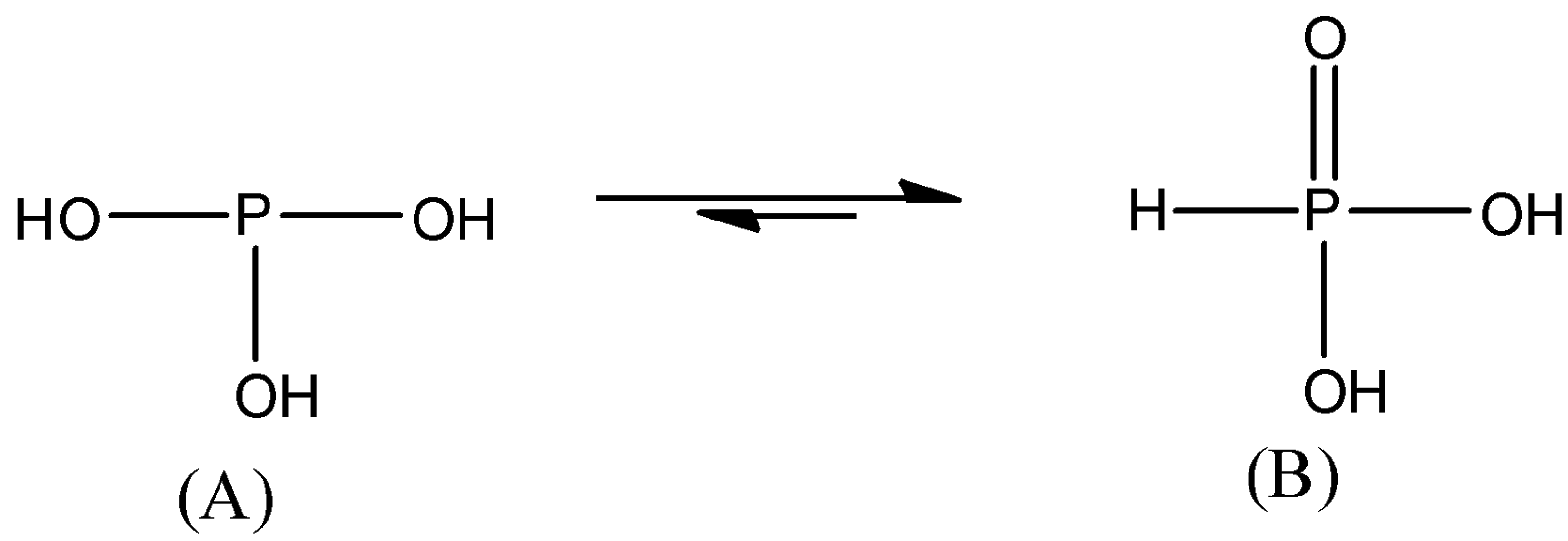
Here, we may think that (A) will be the structure of the orthophosphoric acid but actually, this acid is in equilibrium with two structures in which most of the acid exists in form (B).
-So, in order to examine its basicity, we need to consider structure (B).
-Basicity of an acid is the number of acidic protons it has. Generally, the number of –OH groups present in the acids shows the number of protons it can donate and it is the basicity of the structure.
-So, in structure (B) we can see that there are two acidic protons. So, the basicity of orthophosphoric acid will be two.
Therefore the correct answer is (B).
Note: The structure (B) of the orthophosphoric acid is also known as Phosphonic acid. Do not assume that this acid exists mainly in structure (A) because structure (A) has a basicity of 3. Prefix phosphoric in its acids shows that the phosphorus atom is in a higher oxidation state.
