Question
Question: What is the anhydride of perchloric acid?...
What is the anhydride of perchloric acid?
Solution
An organic acid is a substance that is made up of carbon An organic chemical, anhydride, is an acid anhydride. A molecule with two acyl groups linked to the same oxygen atom is known as an acid anhydride. A carboxylic anhydride is a kind of organic acid anhydride in which the parent acid is a carboxylic acid and the anhydride formula is (RC(O))2O . This form of symmetrical acid anhydride is called by substituting the word acid in the parent carboxylic acid's name with the word anhydride.
Complete answer:
Perchloric acid has the formula HClO4 and is a mineral acid. This colourless chemical, which is usually found as an aqueous solution, is a stronger acid than sulfuric and nitric acids. When heated, it is a potent oxidant, although at ambient temperature, aqueous solutions up to about 70% by weight are typically harmless, with only strong acid characteristics and no oxidising capabilities. Perchloric acid is used to make perchlorate salts, particularly ammonium perchlorate, which is an essential component of rocket fuel. Perchloric acid is extremely corrosive and may easily combine with other chemicals to create explosive combinations.
The chemical compound Cl2O7 stands for dichlorine heptoxide. The anhydride of perchloric acid is chlorine oxide. It is made by carefully distilling perchloric acid in the presence of phosphorus pentoxide, a dehydrating agent:
2 HClO4 + P4O10 → Cl2O7 + H2P4O11
The chlorine(VII) oxide in the mixture may be distilled off. The maximum oxidation number of a Group is stated.
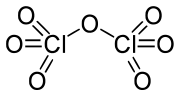
Illumination on chlorine and ozone mixes can also produce it. When anhydrous, it slowly hydrolyzes back to perchloric acid, which is similarly dangerous.
Note:
Cl2O7 , while being the most stable chlorine oxide, is a powerful oxidant and explosive that may be ignited by flame, mechanical stress, or contact with iodine. It is, however, less oxidising than the other chlorine oxides, and when cold, it does not damage sulphur, phosphorus, or paper. It has the same effects on the human body as elemental chlorine and must be handled with the same care.
