Question
Question: What is the action of moist silver oxide on ethyl bromide?...
What is the action of moist silver oxide on ethyl bromide?
Solution
Moist silver oxide acts as a good nucleophile. When it is reacted with ethyl bromide a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution takes place and the product which is formed, is used as a fuel.
Complete step by step answer:
- In order to answer our question, we need to learn about the action of moist silver oxide on alkyl halides. Let us know about the SN2 reaction in detail. Nucleophilic substitution bimolecular or SN2 is a single step bimolecular reaction in which the incoming nucleophile attacks the C-atom of substrate in a direction opposite to the outgoing nucleophile The reaction passes through a transition state in which both the incoming and outgoing nucleophiles are bonded to the same C-atom. In the transition state, the C-atom is sp2 hybridised with a p-orbital whose one lobe overlaps with an orbital of incoming nucleophile and the other lobe overlaps with an orbital of outgoing nucleophile. The three non-reacting atoms or groups attached to the C-atom are nearly coplanar at an angle of 1200 The reaction is completed when the outgoing nucleophile leaves with the bond pair of electrons and simultaneously the incoming nucleophile binds to the C-atom. As the reaction progresses, the configuration of the C-atom under attack is inverted. An SN2 reaction is always accompanied by inversion of configuration. The inversion in configuration implies change in configuration from R to S or S to R (provided the incoming nucleophile and outgoing nucleophile have same priority) and not from (+) to (-) or (-) to (+)
Steric hindrance plays a very vital role in an SN2 reaction. As steric hindrance increases the rate of SN2 reaction decreases Thus for the same halogen the reactivity order of alkyl halides towards SN2reaction is as under: methyl halide>primary alkyl halide>secondary alkyl halide>tertiary alkyl halide.
Now, moist silver oxide reacts via SN2 mechanism. We have the reaction as:
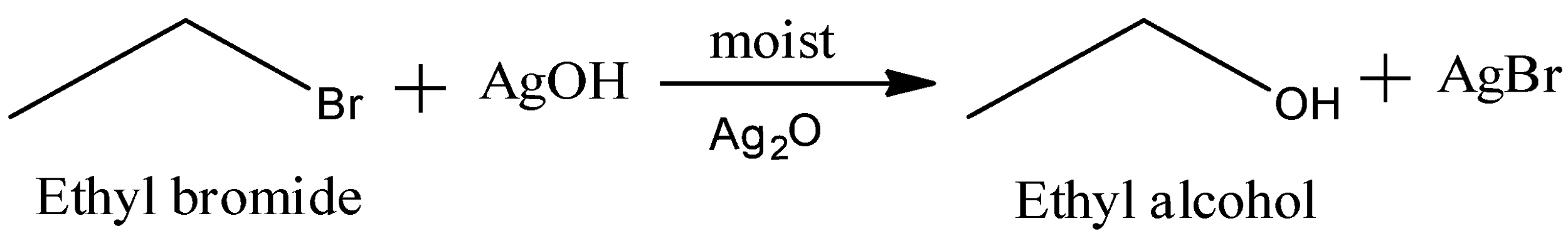
So, we get the major product as ethyl alcohol, and some amount of AgBr is also formed.
Note: For the same alkyl group, the reactivity of alkyl halides increases with the decrease in the C−X bond dissociation energy. Therefore, R−I>R−Br>R−Cl>R−F.
