Question
Question: What is Rosenmund’s reaction? What is the purpose of adding \[BaS{{O}_{4}}\]in this reaction?...
What is Rosenmund’s reaction? What is the purpose of adding BaSO4in this reaction?
Solution
Rosenmund’s reaction is an organic reaction. It is a reduction hydrogenation process. BaSO4 is a catalyst used in this reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
The Rosenmund reaction is a hydrogenation process where molecular hydrogen reacts with the acyl chloride in the presence of catalyst – palladium on barium sulfate.
The Rosenmund reaction is catalyzed by palladium on barium sulfate. The barium sulfate reduces the activity of the palladium due to its low surface area, thereby preventing over reduction. Barium sulfate reduces the activity of palladium due to its low surface area meaning it decreases the reducing power of palladium in order to prevent over-reduction of the acid.
A poison can be added to totally deactivate the palladium catalyst. The need for deactivation arises because the subsequent aldehyde formed from the reduction of the acyl chloride will also be reduced to a primary alcohol by the system. And below reaction chlorine gets replaced by hydrogen. Pd/BaSO4 is the catalyst for this reaction don’t take part in chemical change. Below given is the rosenmund reaction:
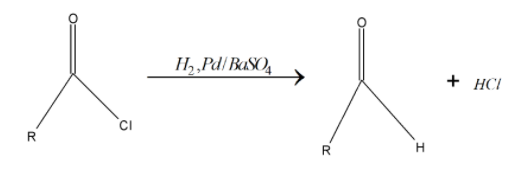
Due to the high reactivity of hydrogen gas it readily initiates a substitution in the acyl chloride, forming HCl and the required aldehyde.
Note:
Common poisons used to limit palladium activity in the Rosenmund technique are thioquinanthrene and thiourea. Pd/BaSO4is known as lindlar’s catalyst.
