Question
Question: What is Primase in DNA Replication?...
What is Primase in DNA Replication?
Solution
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetic material found in humans and nearly all other organisms. Almost every cell in a person's body contains the same DNA. The majority of DNA is found in the cell nucleus (where it is known as nuclear DNA), but a small amount can also be found in the mitochondria (where it is called mitochondrial DNA or mtDNA). Mitochondria are cell structures that convert energy from food into a form that cells can use.
Complete answer:
DNA stores information as a code composed of four chemical bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). Human DNA is made up of approximately 3 billion bases, with more than 99 percent of those bases being the same in all people. The order, or sequence, of these bases, determines the information available for building and maintaining an organism, much like how letters of the alphabet appear in a particular order to form words and sentences.
The ability of DNA to replicate, or make copies of itself, is an important property. Each strand of DNA in the double helix can act as a template for duplicating the base sequence. When cells divide, this is critical because each new cell must have an exact copy of the DNA present in the old cell.
Enzymes involved in DNA replication are:
- Helicase
- Gyrase
- Primase
- DNA polymerase III
- DNA polymerase I
- Ligase
DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3′ OH group of the last nucleotide, not initiate replication. To begin replication, a primer is required. Primase is an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of a short RNA primer needed to begin DNA replication. It creates primers that are complementary to the single strand of DNA.
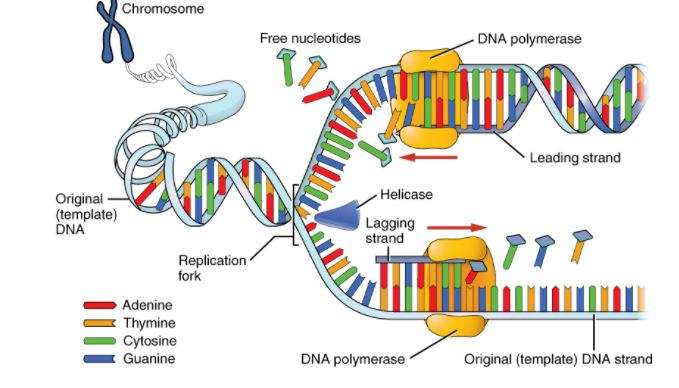
Note: Primase first synthesizes the RNA segments, which are then elongated by DNA polymerase. The alpha DNA Polymerase primase complex is formed when the DNA polymerase forms a protein complex with two primase subunits. Primase is one of the slowest and most error-prone polymerases. Premises in organisms such as E. coli synthesize approximately 2000 to 3000 primers per second. Primase also serves as a halting mechanism, preventing the leading strand from outpacing the lagging strand by halting replication fork progression. The formation of the first phosphodiester bond between two molecules of RNA is the rate-determining step in primase.
