Question
Question: What is photorespiration? Explain the mechanism and its significance....
What is photorespiration? Explain the mechanism and its significance.
Solution
Photorespiration is a process which involves loss of fixed carbon as CO2, in plants in the presence of light it is initiated in chloroplasts. This process does not produce ATP or NADPH and is a wasteful process.
Complete answer:
Photorespiration is usually a wasteful process and is not performed in the C4 plants that are plants that possess kranz anatomy .
Mechanism of photorespiration:
Photorespiration occurs usually when there is high concentration of oxygen.
Under such circumstances, Rubisco, the enzyme that catalyses the carboxylation of RuBP during the first step of the Calvin cycle, functions as an oxygenase.
Some O2 does bind to Rubisco and hence CO2, fixation is decreased.
The RuBP binds with O2, to form one molecule of PGA (3C compound) and phosphoglycerate (2C compound) in the pathway of photorespiration.
There is neither the synthesis of sugar, nor of ATP. Rather, it results in the release of CO2, with the utilisation of ATP. It leads to a 25 percent loss of the fixed CO2, O2, is first utilized in chloroplast and then in peroxisomes.
This process is also called the C2 cycle. This requires organelles such as chloroplast peroxisome and mitochondria .
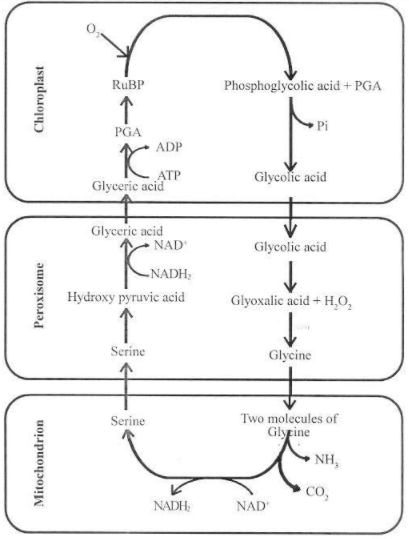
Significance of photorespiration :-
In C4. plants, photorespiration does not occur. This is because these plants have a mechanism that increases the concentration of CO2, at the enzyme site. During the C4 pathway, when the C4, acid from the mesophyll cells is broken down in the bundle sheath cells, it releases con- this results in increasing the intracellular concentration of CO2. This in turn, ensures that the Rubisco functions as a carboxylase minimising the oxygenase activity. Thus, the productivity and yields are better in CA plants as compared to C4, plants. In addition, the C4 plants show tolerance to higher temperature also.
Note: Photorespiration is not related to aerobic respiration as aerobic respiration occurs throughout the day and night in all types of cells, but photorespiration occurs in presence of light in green cells only. ATP is produced in aerobic respiration unlike photorespiration where ATP is consumed. Photorespiration utilizes a part of light energy and saves the plant from photo-oxidative damage.
