Question
Question: What is phagocytosis?...
What is phagocytosis?
Solution
Hint:- It is a process of cell eating where the cell engulfs a particle and after engulfing that particle, that food particle gets digested and this process happens in many organisms for different functions.
Complete answer:
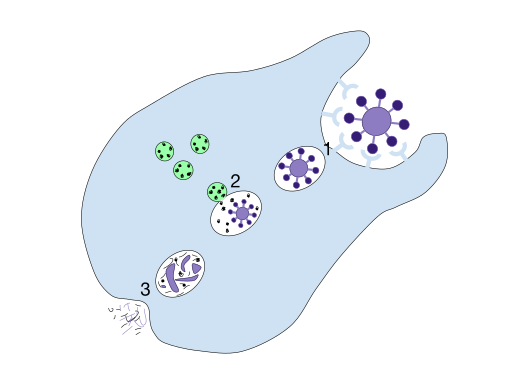
Phagocytosis is a process in which a cell uses its plasma membrane in order to engulf a particle which further after engulfing gives rise to an internal compartment which is called the phagosome. This process happens both in multicellular and in unicellular organisms.
In multicellular organisms, phagocytosis is used in the immune system to remove pathogens and cell debris and in unicellular organisms like amoeba, phagocytosis is used in order to eat and acquire the nutrients.
Process of phagocytosis:
There are 5 steps-
Step 1: Activation of the Phagocyte:
First, the cell which will perform phagocytosis i.e., phagocyte becomes activated due to which the circulating phagocytes produce surface glycoprotein receptors. These glycoprotein receptors increase the ability to adhere to the inner surface of walls and because of this it enables phagocytes to squeeze out of the capillary and get attached to the site of infection.
Step 2: Chemotaxis of Phagocyte:
Chemotaxis is movement of phagocytes towards the increasing concentration of a particular substance and this chemotaxis occurs in the immune system where immune cells pick up chemical signals and migrate towards invading bacteria or the damaged cells.
Step 3: Attachment of phagocyte to the cell or microbe:
In this step, the cell becomes attached to the particle that it will ingest and this attachment is necessary for the ingestion i.e., taking up any substance into the body. This attachment can be unenhanced or enhanced. There are some bacteria which can resist this attachment too and this further becomes hard for them to be taken into the cell and destroyed.
Step 4: Ingestion of the Cell by Phagocyte:
Now, the attachment is done then the cell ingests the particle which is endorsed in a vesicle i.e., phagosome and this phagosome transports this particle into the cell by the help of electron pump into the phagosome.
Step 5: Destruction of the Cell:
Phagocytes contain a membrane sac which is called lysosomes produced by golgi apparatus, this lysosome fuses with the phagosome which contains the ingested microbes and the microbes are destroyed. Due to the presence of hydrolytic enzymes in lysosomes, it breaks down molecules. The cellular waste i.e., the waste which a cell cannot reuse is afterwards discharged from the cell by the process of exocytosis.
Note:-
It is a type of endocytosis where a cell engulfs a particle to form phagosome and this process is mainly done in five steps which are Activation of the Phagocyte, Chemotaxis of Phagocyte, Attachment of phagocyte to the cell or microbe, Ingestion of the Cell by Phagocyte, Destruction of the Cell. An inflammatory response to infection or injury allows these phagocytes to leave the bloodstream and go to the site of infection in order to start phagocytosis.
