Question
Question: What is \(P{H_3}\)?...
What is PH3?
Solution
Phosphine or hydrogen phosphide is a flammable, colourless, extremely toxic gas having a disagreeable garlic-like odour. Moreover, phosphine is classed as pictogen hydride. Phosphine is usually used in semiconductor or plastic industries and even in the production of flame retardants.
Complete answer:
Phosphine is the compound with the chemical formula PH3.
The IUPAC name for PH3 is phosphine. Phosphine is also known as hydrogen phosphide.
Phosphine was first obtained in 1783 by Philippe Gengembre, by heating white phosphorus in an aqueous solution of potassium carbonate.
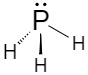
Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure. Length of the P-H bond is 1.42A∘ and the H-P-H bond angle is 93.5∘.
Around the phosphorus atom, there are three sigma bonds and one lone pair.
Explanation of not well defined or absence of PH3 hybridization can be given by Drago’s rule. During the formation of phosphine, the pure p orbitals participate in bonding and avoid getting hybridized.
Phosphine burns to produce a dense white cloud of phosphoric acid.
PH3+2O2→H3PO4
Phosphine dissolves less readily in water but more readily in non-polar solvents.
Phosphine is a Lewis base because of the presence of a nonbonding electron pair on the p- shell that can be donated.
Phosphine can be prepared in many ways. Industrially, it is prepared by the reaction of white phosphorus with potassium hydroxide, producing potassium hypophosphite as a by-product.
3KOH+P4+3H2O→3KH2PO2+PH3
And in the laboratory it can be prepared by disproportionation of phosphoric acid.
4H3PO3→PH3+3H3PO4
Note:
Phosphine has an unpleasant odour like rotting fish and it is a highly toxic respiratory poison. Phosphine is mainly a redox toxin, which can cause cell damage by inducing oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction, while it produces resistance in pests by a mutation in the mitochondrial metabolic gene.
