Question
Question: What is mRNA?...
What is mRNA?
Solution
mRNA stands for messenger RNA. It is a single stranded RNA molecule, which is complementary to
one of the DNA strands of a gene. mRNA is the RNA version of the gene, which leaves the cell nucleus and progresses to the cytoplasm, where proteins are synthesized. During the process of protein synthesis, an organelle known as ribosome moves along with the mRNA.
Complete answer
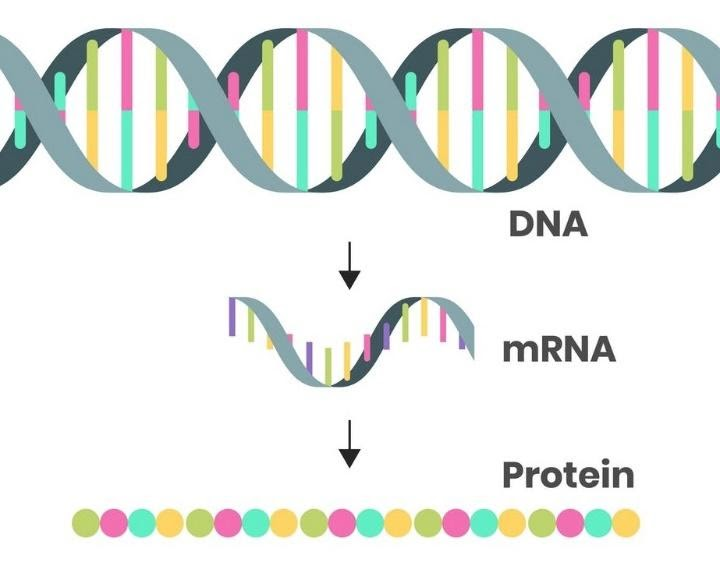
Fig: Synthesis of Protein via mRNA
Ribosome along with mRNA reads its base sequence, and utilizes the genetic code for translating each codon or three-base triplet into its respective amino acid. mRNA carries the genetic information, which are copied in the form of a series of three-base triplets or codons. Each codon is specific to a particular amino acid. Transfer RNA, also called tRNA, recognizes the codon present in the mRNA and calls for the specific amino acid involved in synthesizing the polypeptide chain. Thus, mRNA functions in providing specific binding sites for a series of specific tRNA molecules.
The principal function of mRNA is protein synthesis, which is a two-step process.
During the first step, an mRNA molecule is synthesized on a DNA molecule via the process of transcription. During the second step, the genetic information or message is translated into a linear chain of amino acids via the process of translation. Since, the mRNA is involved in carrying genetic information from nucleus to cytoplasm for the translation process, it is called messenger RNA.
During translation, along with mRNA, other forms of RNA like rRNA and tRNA also participate. rRNA is a component of ribosome and tRNA brings the amino acids for binding for complementary codon-anticodon pairing.
Note:
Generally, one gene, a DNA for a gene, is transcribed into mRNA molecule, which will end up synthesizing one specific protein. Its full form is messenger ribonucleic acid. It is also critical like DNA for the life, by playing a vital role in human biology. Currently, mRNA is used to develop a new category of medicines, by synthesizing and sequencing particular mRNA sequences for diseases.
