Question
Question: What is meant by the term bond order? Calculate the bond order of \[{N_2},{O_2},O_2^ + \] and \[O_2^...
What is meant by the term bond order? Calculate the bond order of N2,O2,O2+ and O2− .
Solution
Bond order is the number of covalent bonds present in a molecule or ion. If we know the molecular orbital structures, it is half the difference between the number of electrons in the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals.
Formula used:
bond order =21[b−a]
Complete step by step answer:
The bond order shows the number of chemical bonds exist between a pair of atoms. From the formula of the bond pair, we can describe it as one half of the difference between the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals and antibonding molecular orbitals.
Bond order formula can be written as:
Bond order =21[b−a]
Where, a is the number of electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals
And b is the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals.
Let us calculate bond order of different molecules given using this formula and their electronic configuration.
A.For N2
As we know, electronic configuration of N2 is σ1s2σ∗1s2σ2s2σ∗2s2π2px2π2py2σ2pz2
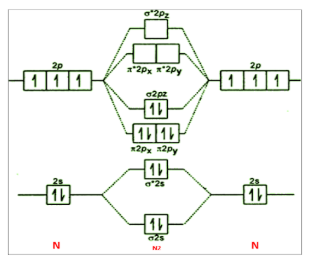
From this we can see there are four electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals and total ten in bonding molecular orbitals. Putting these in the formula, we get
Bond order of N2=21[10−4]=3
Hence, the bond order of nitrogen is 3.
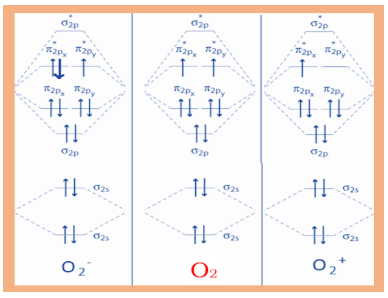
B.For O2
As we know, electronic configuration of O2 is σ1s2σ∗1s2σ2s2σ∗2s2π2px2π2py2σ2pz2π∗2pxπ∗2py
From this we can see there are four electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals and total eight in bonding molecular orbitals. Putting these in the formula, we get
bondorderofO2=21[8−4]=2
Hence, bond order of oxygen is 2.
C.For O2+
As we know, electronic configuration of O2+ is σ1s2σ∗1s2σ2s2σ∗2s2π2px2π2py2σ2pz2π∗2px
From this we can see there are one electron in antibonding molecular orbitals and total six in bonding molecular orbitals. Putting these in the formula, we get
Bond order of O2+=21[6−1]=2.5
Hence, bond order O2+ of 2.5
D.For O2−
As we know, electronic configuration of O2− is σ1s2σ∗1s2σ2s2σ∗2s2π2px2π2py2σ2pz2π∗2px2π∗2py
From this we can see there are seven electrons in antibonding molecular orbitals and total ten in bonding molecular orbitals. Putting these in the formula, we get
Bond order of O2−=21[10−7]=1.5
Hence, the bond order of O2− is 1.5.
Note:
We can also find out bond order using Lewis concept. Firstly, from the structure of the molecule, count the total number of electrons. Then count the number of bond groups between individual atoms and on dividing both, we get bond order of that particular molecule.
