Question
Question: What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case. (i). cyanohydr...
What is meant by the following terms? Give an example of the reaction in each case.
(i). cyanohydrin
(ii). Acetal
(iii). semicarbazone
(iv). Aldol
(v). Hemiacetal
(vi). oxime
(vii). ketal
(viii). Imine
(ix). 2,4 -DNP derivative
(x). schiffs base
Solution
The chemical properties of aldehyde and ketone are due to the carbonyl group present in the molecules. The boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are higher than the non-polar compounds or weakly polar compounds such as ethers but of comparable molecular masses.
Complete answer:
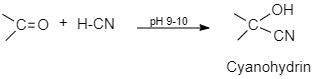
(i). Cyanohydrin: General formula- R2C(OH)CN . Hydroxynitrile is a functional group found in compounds that have a cyano and a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the same carbon atom.
Cyanohydrins are formed when ketone or aldehyde is treated with hydrogen cyanide, sodium cyanide is present in excess as a catalyst.
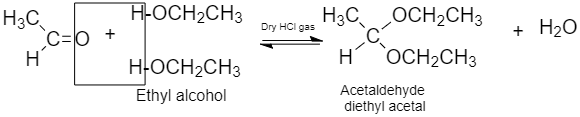
(ii) Acetal: Compounds in which the two alkoxy groups are present at the terminal carbon atom are known as acetals.
It is formed when aldehyde with two equivalents is added to two equivalents of monohydric alcohol in the presence of dry HCl gas.
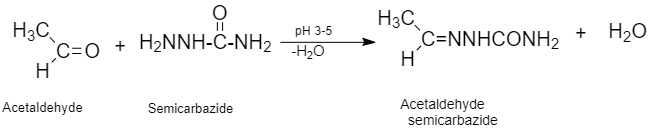
(iii) Semicarbazone: It is a derivative of imines and is produced by a condensation reaction between an aldehyde/ketone and semicarbazide in a weak acidic medium.
(iv) Aldol: is beta hydroxy aldehyde or ketone Aldol is obtained by condensation of two molecules of aldehyde or ketone in the presence of dilute aqueous base.
2CH3CHOOH−CH3CHOHCH2CHO
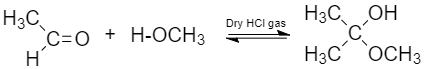
(v) Hemiacetal: They are produced by reaction of alcohol with aldehyde or ketone in the presence of dry HCl gas.
(vi)Oxime: oximes are produced by the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with hydroxylamine.
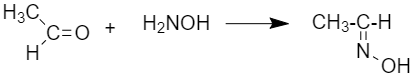
(vii) Ketal: are gem-dialkoxy alkanes, the two alkoxy groups are present on the same carbon. It is obtained when ketone reacts with ethylene glycol in the presence of dry HCl gas.
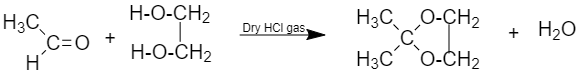
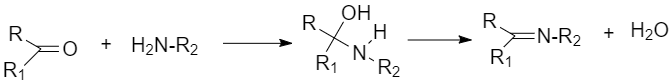
(viii) Imine: They are chemical compounds containing a carbon-nitrogen double bond. And it is obtained by the reaction between aldehyde or ketones with ammonia derivatives.
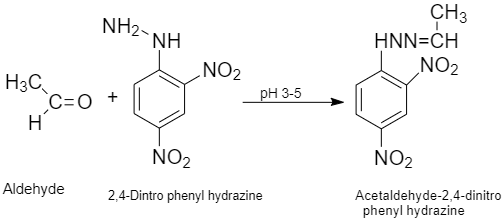
(ix) 2−4 DNP derivative: are obtained when aldehydes or ketones react with 2,4 - dinitrophenyl hydrazine in a weak acidic medium.
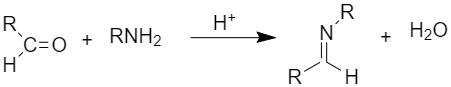
(x) Schiff’s base is obtained when aldehydes or ketones react with primary amines (aliphatic or aromatic)
Note:
Exceptional Lower aldehydes have unpleasant odor but aldehydes and ketones generally have pleasant smell. With the increase in molecule size, the odor becomes less pungent. Benzaldehyde provides an odor like almonds and cinnamaldehyde is used as a flavoring agent.
