Question
Question: What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction. 2,4-DNP derivative...
What is meant by the following term? Give an example of the reaction.
2,4-DNP derivative
Solution
2,4-DNP is the abbreviated name of 2,4- dinitrophenyl hydrazine. 2,4-DNP is also known as Brady’s reagent. A derivative is a substance that is formed when the main reagent (as in this case it is 2,4-DNP) reacts with some chemical compound. To attain a derivative a molecule has to be eliminated that eventually forms the product. The reaction must be an Elimination reaction.
Complete answer:
We’ve seen the definition of a derivative. Let’s understand the formation of the 2,4-DNP derivative.
The 2,4-DNP derivative is formed when 2,4-Dinitrophenyl hydrazine reacts with a carbonyl compound namely an aldehyde or a ketone in a weakly acidic medium. It leads to the formation of a 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazone.
In simple words, we can say that it is substituted hydrazine.
The reaction for the formation of the 2,4-DNP derivative is as follows:
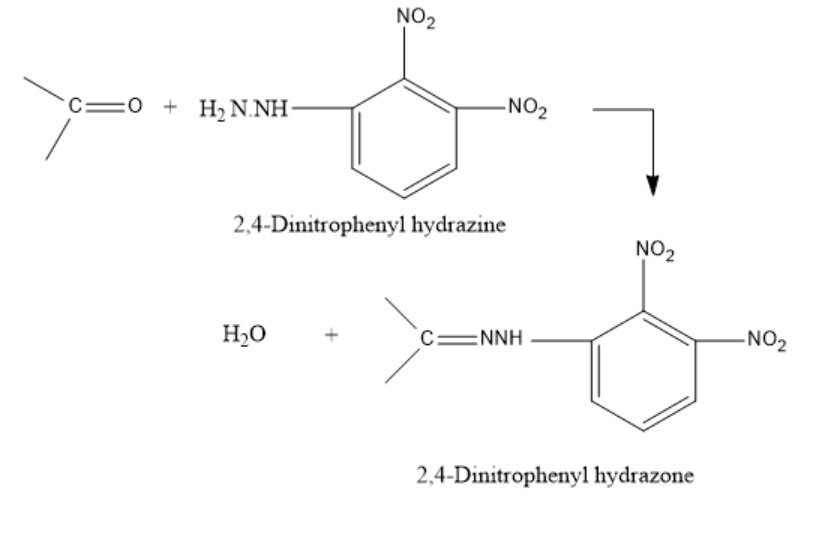
The groups attached to the carbonyl carbon can be both alkyl groups (ketones) or one alkyl and one hydrogen (aldehydes).
2,4-DNP is used as a test to find aldehydes or ketones. It forms bright orange colour crystals called 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazone on reaction with carbonyl compounds. If 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine is formed as a precipitate, we can say that there is a presence of a carbonyl compound. The crystals are filtered and purified by recrystallization.
2,4-DNP derivatives have different melting points. They are compared to the melting points of 2,4 DNP to identify the presence of carbonyl compounds.
Let us now see a reaction for the formation of 2,4-DNP derivative:
If Propanone reacts with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine in a weakly acidic medium of pH-3.5 then, Propanone,2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone will be prepared.
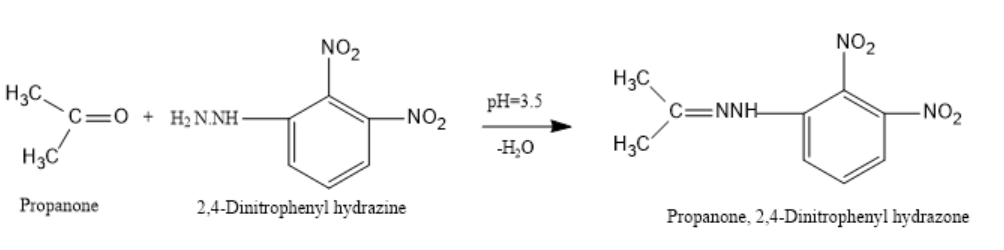
Note:
2,4-Dinitrophenyl hydrazine derivative distinguishes between aldehyde and ketone by the presence of a hydrogen bond in aldehyde. Ketones do not contain a hydrogen bond. The hydrogen bond present oxidizes the aldehydes, as they are fast reducing agents.
