Question
Question: What is meant by ‘shape selective catalysis’?...
What is meant by ‘shape selective catalysis’?
Solution
In a reaction, some outer species take part which enhance the rate of reaction. They are not consumed themselves. Such species are called catalysts and the process is called catalysis. When the catalysis occurs due to the shape of the molecule, then the process becomes shape selective catalysis.
Complete step by step answer:
-The compounds which are present before the reaction occurs are called the reactants. Compounds formed after the reaction are called products. There are certain species that help the reaction to occur and therefore increase the rate of the reaction. Such species are called catalysts.
-Catalysis is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as catalyst. One thing to note is that the catalyst is not consumed in the reaction process. It just enhances the rate of reaction. It is added in a small amount in the reaction chamber.
-As the catalysts increase the rate of reaction, it is very important for them to be able to interact properly with the reactants. So, the catalysts must be of the order of the reactants and in such a shape so as to ensure maximum surface area coverage.
-So, shape selective catalysis is a catalytic reaction which depends on the shape and structure of the catalyst and also on the size of the reactant as well as product molecules. It plays a very important role in the synthesis of organic chemicals as well as for processing of petroleum and fuels.
-The best example of this type of catalysis is the catalysis by zeolites. The pore size of the zeolites ranges from 260-740 pm. So, the molecules with size less than this can only enter the zeolites and those with greater size cannot penetrate through the zeolites. Once the molecules enter the zeolite, reaction occurs. Thus, this ensures that we obtain the desired products only. The addition of impurities becomes very less in such processes.
-An example of zeolite catalysis is ZSM. ZSM (5) is a zeolite sieve which has the porosity of 5, as the name suggests. It is extensively used to convert alcohols into hydrocarbons. Thus, the selectivity of the catalyst plays an important role in the completion of the reaction generating the desired products.
-ZSM-5 is also used for the isomerization of m-xylene. It is selective for p-xylene and thus, only m-xylene reacts. The most selective catalysts for this process were found by the process of gas-phase isomerization reaction. The process was studied for various catalysts like Ni, Sn, Pt, Ga, Zr. Among them, Ga and/or Pt was found to be the most active.
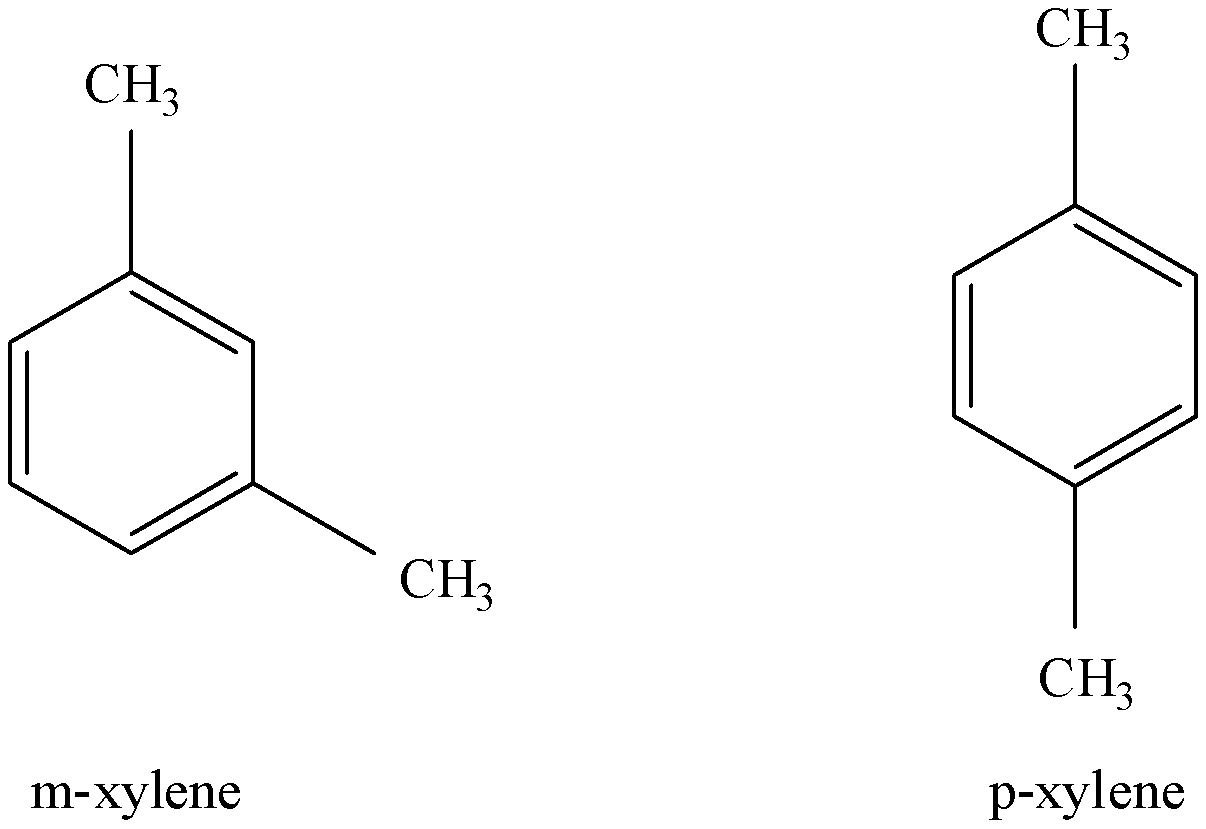
m-xylene is selected for reaction due to its shape.
Note: Catalysts are of two types – positive catalysts and negative catalysts. Positive catalysts increase the rate of reaction while negative catalysts decrease the rate of the reaction. Both of them have different roles in reactions. Positive catalysts decrease the time duration of the reaction. Negative catalysts are used mainly if the compound is too reactive and we need to make a certain product and stop it from reacting further.
