Question
Question: What is meant by hybridization of atomic orbitals? Describe \( sp,s{p^2}\,and\,s{p^3} \) hybridizati...
What is meant by hybridization of atomic orbitals? Describe sp,sp2andsp3 hybridization with examples.
Solution
Hint : Hybridization is defined as the mixing of a group of slightly different atomic orbitals, resulting in a new set of orbitals with equivalent energies and forms. One 2s orbital, for example, can combine with two 2p orbitals of carbon to generate three new sp2 hybrid orbitals. Because there is less repulsion between the electron pairs in these hybrid orbitals, they are more stable. Hybridization aids in determining the molecule's geometry.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
sp Hybridization:
When one s and one p orbital in the same main shell of an atom combine to generate two new equivalent orbitals, this is known as sp hybridization. sp hybridised orbitals are the new orbitals that develop. It produces 180 -degree linear molecules.
This sort of hybridization entails combining one s and one p orbital of equal energy to create a new hybrid orbital known as a sp hybridised orbital.
Diagonal hybridization is another name for sp hybridization.
Each sp hybridised orbital has 50 percent s and p character.
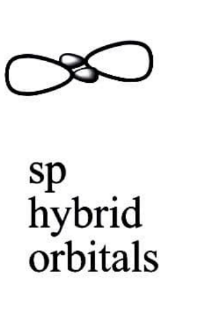
All beryllium compounds such as BeF2, BeH2, BeCl2 and all carbon-containing triple bond compounds such as C2H2 are examples of sp Hybridization.
sp2 Hybridization:
When one s and two p orbitals of the same shell of an atom combine to generate three equivalent orbitals, this is known as sp2 hybridization. sp2 hybrid orbitals are the new orbitals that have been created.
Trigonal hybridization is another name for sp2 hybridization.
It entails combining one s orbital with two p orbitals of equal energy to create the sp2 hybrid orbital.
A trigonal symmetry blend of s and p orbitals is maintained at 1200 degrees.
All three hybrid orbitals remain in the same plane and form a 120∘ angle with one another. Each of the resulting hybrid orbitals has 33.33 percent s and 66.66 percent character.
A triangle planar form is found in molecules in which the central atom is connected to three other atoms and is sp2 hybridised.
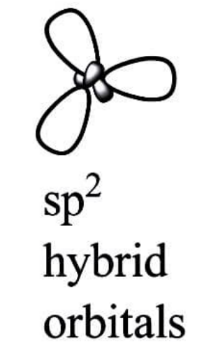
Examples:
BF3, BH3, and all other Boron compounds
Ethylene is a group of carbon molecules that have a carbon-carbon double bond (C2H4)
sp3 Hybridization:
A tetrahedral hybridization, or sp3, occurs when one orbital and three orbitals belonging to the same shell of an atom combine to generate four new equivalent orbitals. sp3 hybrid orbitals are the new orbitals that have been generated.
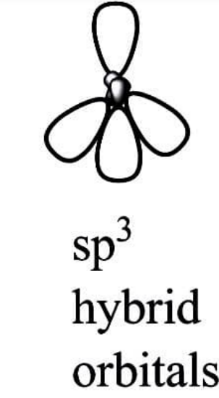
These are aimed at the four corners of a conventional tetrahedron and form a 109∘28′ angle with each other.
The sp3 hybrid orbitals have a 109.280 degree angle between them.
Each sp3 hybrid orbital contains 25% s character and 75% p character.
Ethane (C2H6) and methane are two examples of sp3 hybridization.
Note :
The hybrid orbitals have a different geometry of orbital arrangement and energy than the conventional atomic orbitals after hybridization. In addition, the orbital overlap reduces the molecule's energy. Degenerate hybrid orbitals are generated by combining conventional atomic orbitals with degenerate hybrid orbitals.
