Question
Question: What is meant by crystal field splitting energy? On the basis of crystal field theory, write the ele...
What is meant by crystal field splitting energy? On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of d4 in terms of t2g and eg in an octahedral field when
A. Δ0>P
B. Δ0<P
Solution
Δ0 is the crystal field splitting energy and P is the pairing energy. When Δ0>P, it is a strong field ligand. When Δ0<P, it is a weak field ligand.
Complete step by step answer:
The theory that explains the structure and the stability of the coordination complexes is known as the crystal field theory.
The assumptions of crystal field theory are as follows:
1. The metal ion is considered to be a positive charge.
2. The ligands are considered to be a negative charge.
The elements of the d-block of the periodic table have variable oxidation states and variable coordination number. Thus, the coordination complexes are formed by the d-block elements of the periodic table.
The d-subshell has five degenerate orbitals.
When the ligand bonds to the metal ion, the energy of the degenerate d-orbitals increases.
As the energy of the degenerate d-orbitals increases, the degenerate orbitals split into t2g and eg orbitals.
The difference in the energies of the t2g and eg orbitals is known as the crystal field splitting energy (CFSE). It is denoted by Δ0.
The splitting of degenerate d-orbitals is shown in the diagram below:
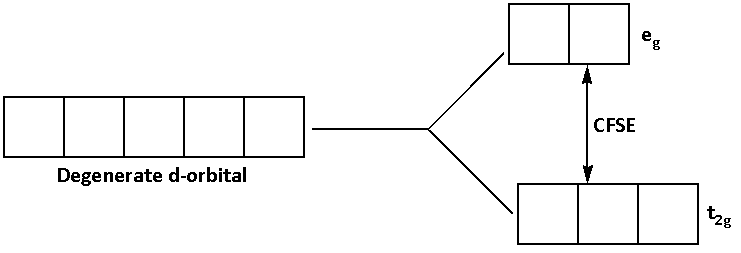
The splitting of the energy depends on the type of the ligand. If the ligand is a strong field ligand its splitting energy is high and if the ligand is a weak field ligand its splitting energy is low.
Write the electronic configuration of d4 in terms of t2g and eg in an octahedral field when Δ0>P as follows:
1.When Δ0>P i.e. crystal field splitting energy is greater than the pairing energy, the ligand is a strong field ligand. When the ligand is a strong field ligand, the fourth electron pairs in the t2g orbital.
Thus, the electronic configuration is as follows:
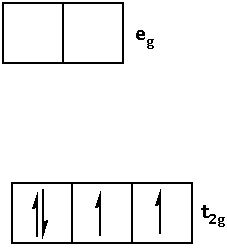
Write the electronic configuration of d4 in terms of t2g and eg in an octahedral field when Δ0<P as follows:
2.When Δ0<P i.e. crystal field splitting energy is smaller than the pairing energy, the ligand is a weak field ligand. When the ligand is a weak field ligand, the fourth electron jumps in the eg orbital.
Thus, the electronic configuration is as follows:
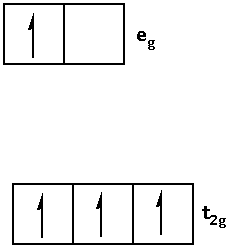
Note:
Strong field ligands form low spin complexes. The examples of strong field ligands are CO−, CN−. Weak field ligands form high spin complexes. The examples of weak field ligands are F−, Cl−.
