Question
Question: What is meant by a substitution reaction? Give an example (with equation) of the substitution reacti...
What is meant by a substitution reaction? Give an example (with equation) of the substitution reaction of an alkane.
(b) How is soap made? Write a word equation involved in soap making.
Solution
A substitution reaction is also known as a single displacement reaction, single replacement reaction, or single substitution reaction. When one or more atoms or groups of atoms in a molecule are replaced or substituted by other atoms or groups of atoms, substitution processes occur.
Complete answer:
(a) A substitution process occurs when one (or more) hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon are replaced by other atoms (such as chlorine).
Example: Methane interacts with chlorine to generate chloromethane and hydrogen chloride in the presence of sunshine, forming chloromethane and hydrogen chloride.
CH4+Cl2sunlightCH3Cl+HCl
b.) Soap is manufactured by heating animal fat or vegetable oils with sodium hydroxide.
Fatoroil+SodiumhydroxideHeatSoap+Glycerol
C2H5OH+CH3COOH=CH3COOC2H5+H2O
CH3COOC2H5+NaOH=C2H5OH+CH3COONa
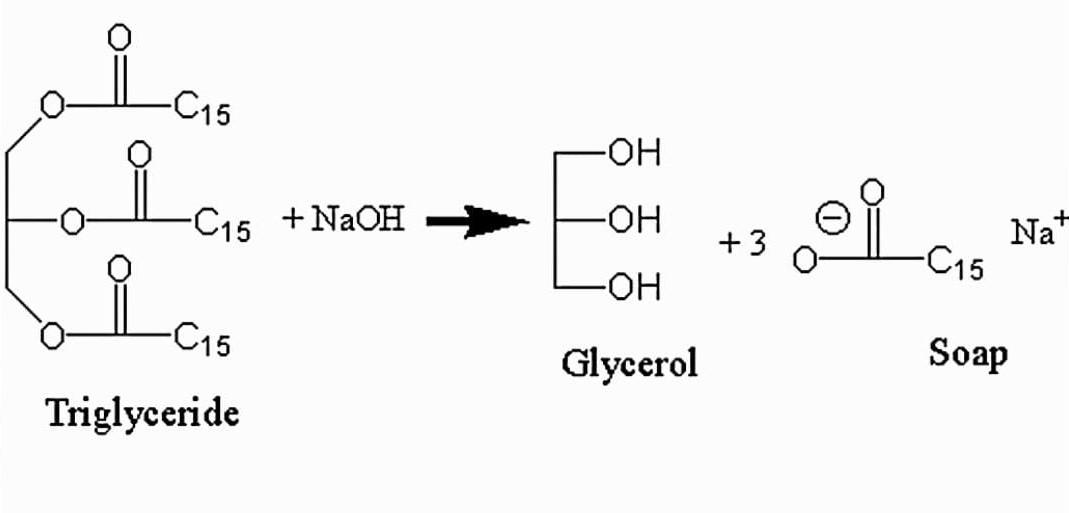
Saponification is the name of the procedure. Saponification is the process of converting fat, oil, or lipid into soap and alcohol using an aqueous alkali solution (e.g. NaOH) . Soaps are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains that are salts of fatty acids. Sodium oleate is a common soap.
Additional Information:
The amount of base necessary to saponify a fat sample is known as the saponification value. To account for the unknown saponification value discrepancy between their oil batch and laboratory averages, soap producers formulate their formulas with a modest lye shortfall.
Note:
Alkenes are rarely substituted because every unsaturated molecule aspires to become saturated and hence undergoes addition. Benzene is the only exception. Most aromatic compounds, such as furan and pyrrole, contain resonance, which gives them exceptional stability. To prolong their conjugation, they go through replacement.
