Question
Question: What is hybridization? Explain \(s{{p}^{3}}\) hybridization with an example....
What is hybridization? Explain sp3 hybridization with an example.
Solution
Mixing of two different entities to get another entirely different entity is the general meaning of the term hybridization. The concept is also followed by atomic orbitals. Then, depending on the number and type of orbitals involved, there are different types of hybridization.
Complete Solution :
Hybridization is defined as mixing of two atomic orbitals of same or nearly same energies to get new orbitals of equivalent energy. These new orbitals are called hybrid orbitals. However, certain rules are followed while hybridization of orbitals occurs. These are as follows –
- Only central atom orbitals can undergo hybridization.
- To form a new hybrid orbital, participating atomic orbitals should be of the same energy.
- The number of hybrid orbitals formed is always equal to the sum of the number of participating atomic orbitals.
- The hybrid orbitals are scattered in space and tend to be farthest apart.
- Hybridised bonds are stronger than non-hybrid ones.
sp3 type of hybridization – When one s- and the p- orbitals of the same atomic orbitals mix to give new hybrid orbitals of equivalent energy, sp3 type of hybridization is observed.
Characteristic features of sp3 type of hybridization are –
- The orbitals are directed towards four corners of a regular tetrahedron.
- All orbitals make an angle with each other.
- Each hybrid orbitals have 25% s character and 75% p character.
Simple example of sp3 hybridization is ethane molecules.
- In ethane, s,px,py and pz orbitals of both the carbon atoms undergo sp3 hybridization to give 4 hybrid orbitals with equal energy each. Among these orbitals, one hybrid orbitals of one carbon overlaps with 1s orbital of hydrogen and gives 3 sigma bonds. Last orbital overlaps with one sp3 orbital of another carbon atom and gives a sigma bond between the two carbon atoms.
Similarly, sp3 hybridization is observed in methane molecules. The s,px,py and pz orbitals of carbon atom undergo sp3 hybridization to give 4 hybrid orbitals with equal energy. Among these orbitals, one hybrid orbitals of one carbon overlaps with 1s orbital of hydrogen and gives 4 sigma bonds. This is shown below,
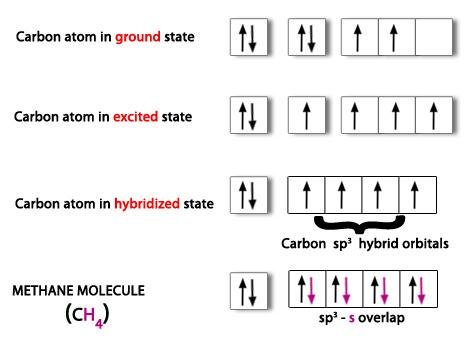
Note: Note that mixing of one s- orbital with 3 p- gives, sp3 one s- and two p- orbitals gives sp2 whereas. Mixing of one s- and one p- gives sp hybridization.
