Question
Question: What is glycogenolysis?...
What is glycogenolysis?
Solution
Glycogen is the polymeric form of glucose molecules. The glucose which is present in excess in the blood is going to convert into glycogen by insulin. Generally Glycogenolysis occurs in the liver to generate glucose.
Complete step by step answer:
Glycogenolysis means conversion of glycogen polymer into individual glucose units.
Glycogen is generally stored in the liver and muscles.
During glycogenolysis, glycogen is going to convert into glucose-1- phosphate and later into glucose-6-phosphate.
Glycogen is a polymer structure containing glucose as the basic monomer.
In glycogenolysis initially glucose molecules are hydrolyzed from the chain, and liberate glucose-1-phosphate as a product. Later the phosphate group is moved to the C-6 position and forms glucose 6-phosphate.
Later glucose 6-phosphate is going to convert into glucose by liver and kidney.
The flow chart showing the glycogenolysis is as follows.

here Pi = inorganic phosphate.
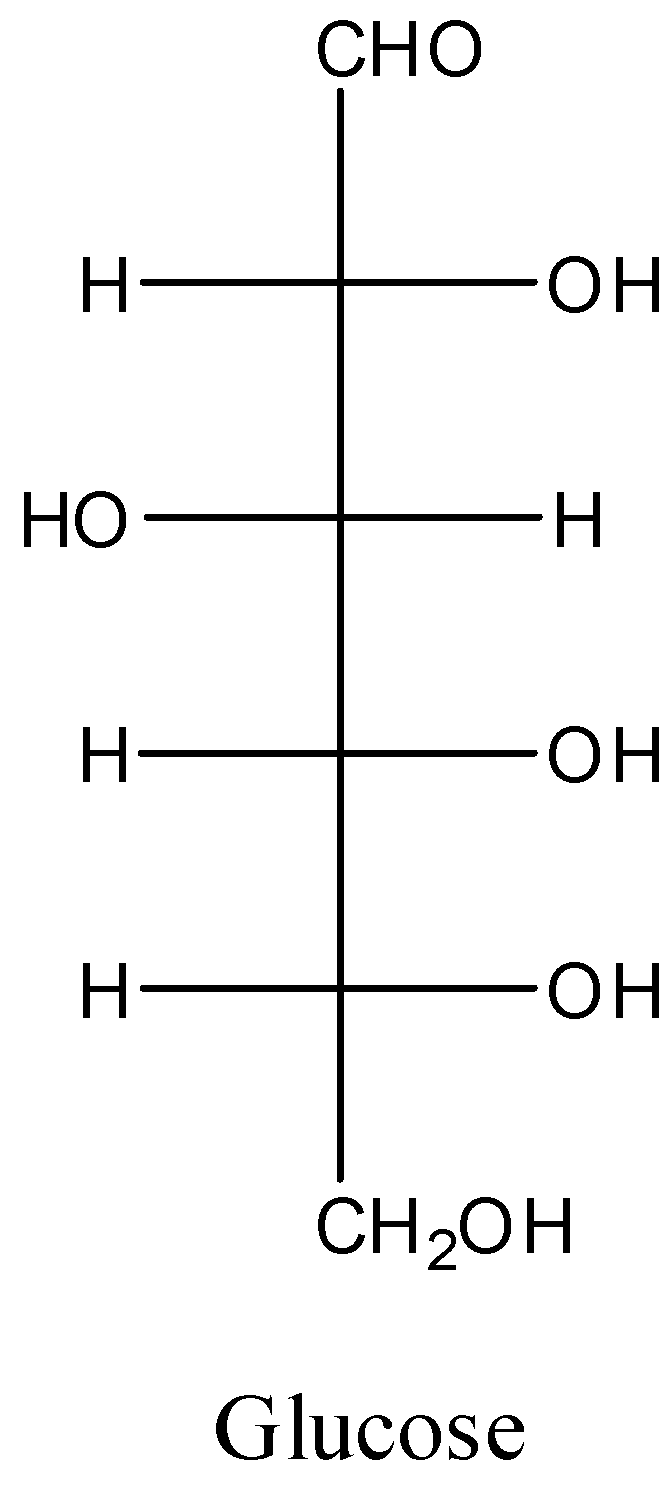
The structure of glucose is as follows.
Additional Information:
Glycogen is stored in the liver, around 5 percent of the liver weight. Whereas glycogen stored in the muscles is around 1-2 percent of their weight.
Generally glycogenolysis happens in the liver. The glucose that is formed from glycogen is not directly used by the liver. Instead, glucose enters the bloodstream and can be used by other cells in the body. Glycogen present in animals is similar to starch present in plants.
Note: The process of converting glycogen into glucose is called glycogenolysis. The process of preparation of glycogen from glucose is called glycogenesis. Lysis means fragmentation. Glycogenolysis means fragmentation of glycogen into glucose.
