Question
Question: What is essentially the difference between \({ {\alpha - }}\) glucose and \({ {\beta - }}\) glucose?...
What is essentially the difference between α− glucose and β− glucose? What is meant by pyranose structure of glucose?
Solution
In the above question it is asked about the difference between α− glucose and β− glucose and the meaning of pyranose structure of glucose. α− glucose and β− glucose differ in –OH group position on carbon 1 of glucose. Pyranose is a polysaccharide structure. This pyranose consists of rings of six atoms.
Complete step-by-step answer: In the above question, we are asked about the difference between α− glucose and β− glucose.
Let us look at their structure:
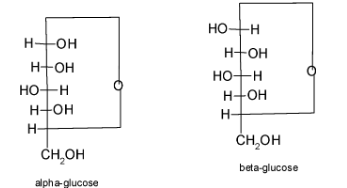
We can clearly see that the structures are almost identical, except that in the α glucose, the –OH group on the far right is facing downward whereas in the β− glucose, it is facing upwards.
Hence, we can say that they are the members of a class of stereoisomers called anomers. Anomers are capable of interconverting in solution. All cyclic structures of monosaccharides exhibit α and β versions.
Pyranose is a polysaccharide structure which does not contain any double bonds. This pyranose consists of rings of six atoms or in other words, it is described as a six membered ring structure. It consists of 5 carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. The pyranose structure of glucose is:
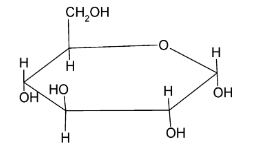
Note: α− glucose and β− glucose are two anomers. We can see that in the beta anomer the large groups are always pointing along the less hindered side whereas in the alpha anomer, one of the groups is pointing towards the more hindered side. Hence, beta glucose is lower in energy and more stable or in other words, alpha glucose has higher energy content.
