Question
Question: What is coenocytic mycelium?...
What is coenocytic mycelium?
Solution
Coenocytic refers to a structure of an organism or an organism itself, that has multiple nuclei in a continuous protoplasmic mass, enclosed by a cell membrane or cell wall. This condition is generally found in the case of algae or fungi.
Complete answer:
A majority of fungi are filamentous in their form. Meaning, they constitute long thread-like structures that are known as Hyphae. And a collection of hyphae is called Mycelium (Plural-mycelia). These mycelia can either be septate or coenocytic. Look at the diagram below:
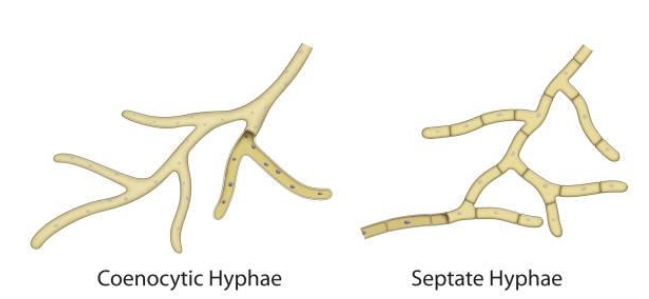
Fig: Types of Hyphae
Concerning the diagram, the first set of hyphae has multiple nuclei (shown by the dark dots) in a continuous mass of protoplasm. This condition gives rise to the multinucleated or coenocytic condition, where several nuclei are enclosed by a cell wall in a continuous (undivided) mass of protoplasm.
In contrast, the second image shows a clear discontinuity in the protoplasm. And each divided section has one nucleus. This kind is known as Septate hyphae.
Now as we have stated earlier, that a collection or network of hyphae is known as Mycelium, so if the network is constituted by coenocytic hyphae, then such a Mycelium is known as Coenocytic Mycelium. Or simply to define it, a Coenocytic Mycelium is a network of multinucleated hyphae.
Here are some of the properties of a Coenocytic mycelium:
- Multinucleate
- Aseptate (lacks septa)
- Coordination
Additional information:
Coenocytic Mycelium is a characteristic feature of Phycomycetes.
Note: It has to be noted that the phenomenon of Coenocytic is not to be confused with Syncytium. The coenocytic condition arises when a cell fails to undertake cell division after the nuclear division. Syncytium occurs due to the fusion of multiple cells.
