Question
Question: What is Catenation? Write the structural formulae of the following: a) Cyclopropane b) Ethane ...
What is Catenation? Write the structural formulae of the following:
a) Cyclopropane
b) Ethane
c) Isobutane
Solution
Hint: Carbon shows the property of catenation. It can form long chains due to its valency 4. Due to this property vast no. of organic compounds are formed.
Complete step by step answer:
Binding of an element itself through covalent bonds in order to form chain and ring molecules are called Catenation. Carbon exhibits catenation property. It forms long hydrocarbon chains and rings like benzene. The bonds formed are covalent bonds. The ability of an element to possess the property of catenation is based on the bond energy of the element, which decreases with more diffused orbitals overlapping to form the bond. Carbon has least diffused valence shell p orbital which is capable of forming longer p-p sigma bonded chains of atoms than in heavier atoms. Catenation property is also influenced by a range of steric and electronic factors, including electronegativity of the element etc.
Sulphur can catenate to form monoclinic sulphur or S8 molecule. On heating these rings will open and can give rise to even longer chains.
Selenium and Tellurium also show catenation to a small extent.
Silicon can also form sigma bonds with other silicon atoms and form long chains. Its analogues to hydrocarbons are called silanes.
Structural formulae of
(A)Cyclopropane is C3H6
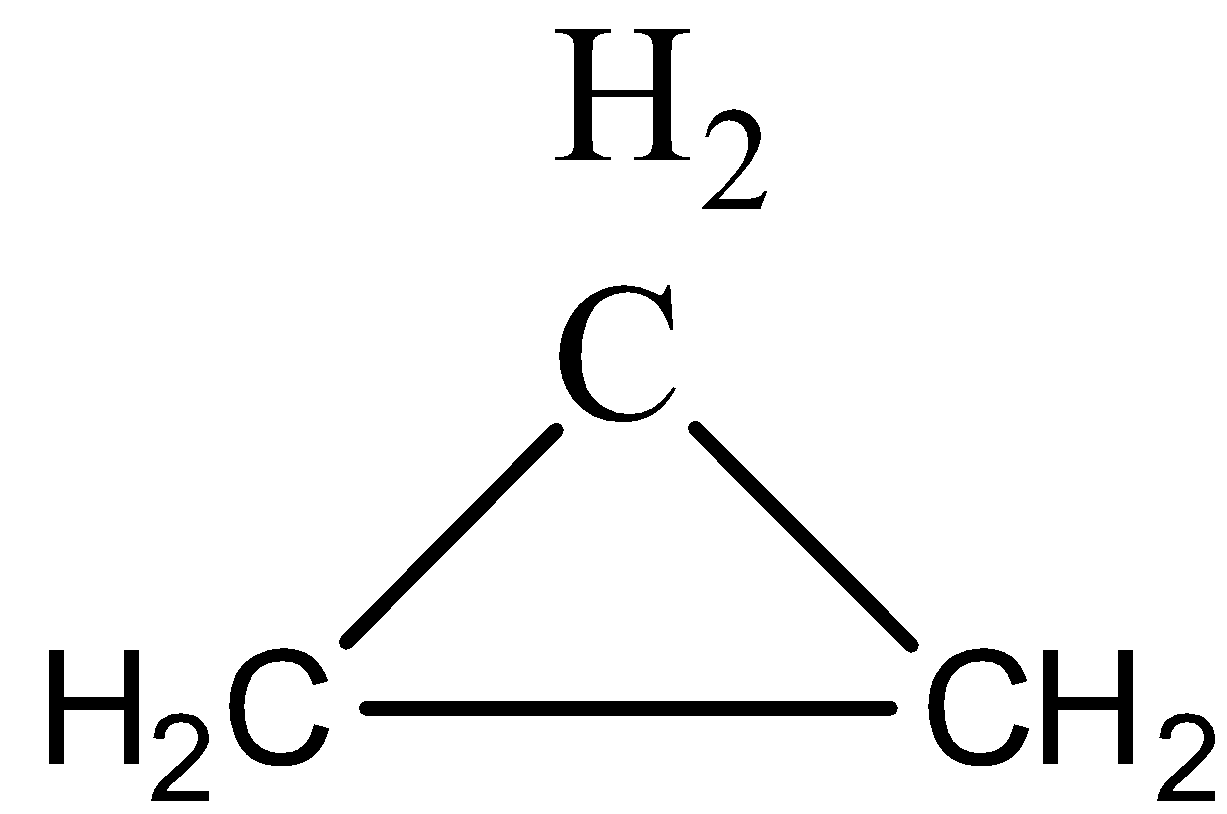
(B)Ethane is C2H6
H3C−CH3
(C)Isobutane is C4H10
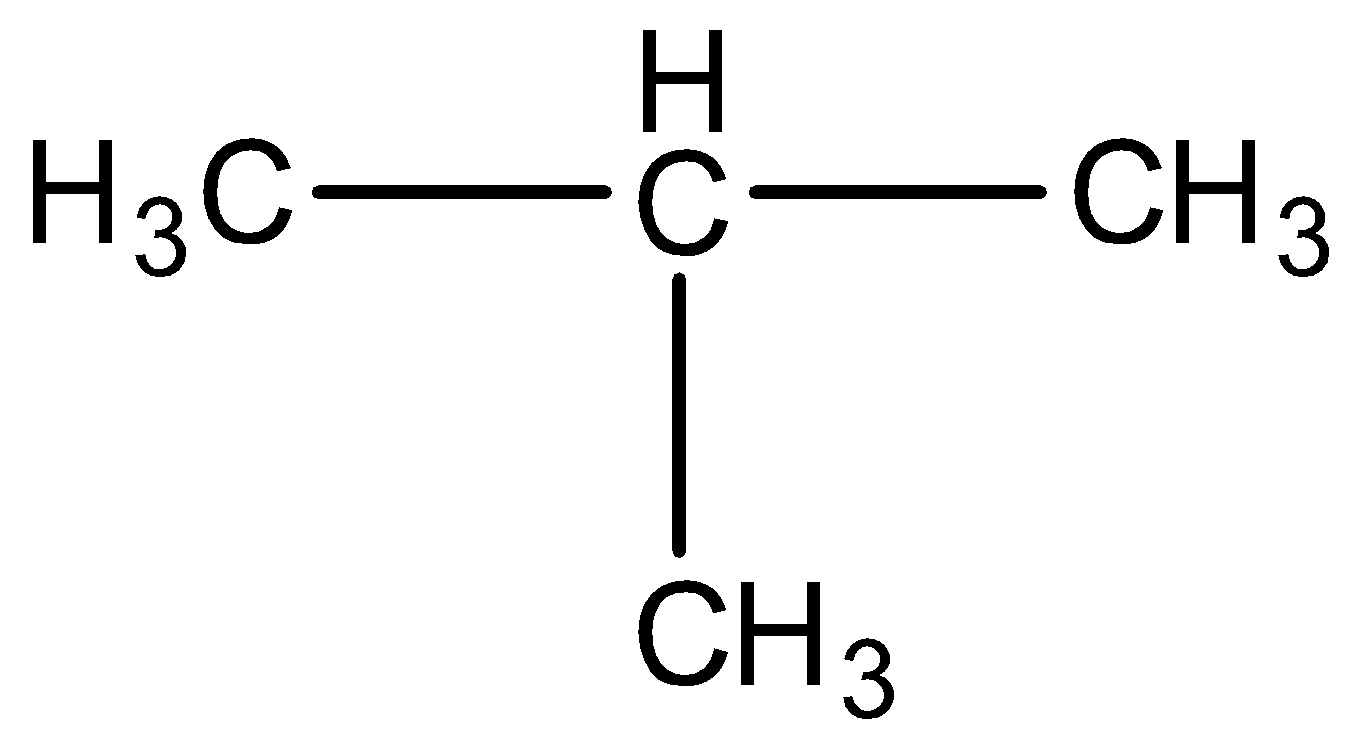
Structural formula is straight lines connecting the atomic symbols which are used to represent single bond, two such lines to represent double bond and 3 lines for triple bond. Such representations of a compound is called structural formula of a compound
Note: Structural formula is a way of representing chemical compounds. While writing the structural formula, we need to check the number atoms that are present and how they are bonded in the molecule. It is derived from the IUPAC name.
