Question
Question: What is called Central Dogma in molecular biology?...
What is called Central Dogma in molecular biology?
Solution
Molecular biology, including molecular synthesis, alteration, mechanisms, and interactions, is the branch of biology that concerns the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells.
Complete answer: The core dogma explains the flow of cell genetic material, the replication of DNA, and the coding of RNA via the transcription process, and further translation of RNA codes for proteins.
Through the context, it is possible to grasp the idea of a series of interactions. Biopolymers are among the most common. Proteins, RNA, and DNA, which are further classified into general transfers, unknown transfers, and special transfers, are the main categories of biopolymers.
In an unusual circumstance in the laboratory, special transfers occur. In virtually all cells, a general transition occurs. The normal flow of information through transcription and translation is described. Transfers that are unknown are said to never occur.
Steps in Core Dogma-
In two separate steps, the core dogma takes place:
Transcription- This is the mechanism through which the RNA polymerase enzyme transfers information from a single strand of DNA to RNA. There are three parts of the DNA strand that undergo this process, namely the promoter, the structural gene, and the terminator.
Translation- This is the mechanism by which the RNA codes for particular proteins. It is an active process in which energy is needed. The charged tRNA molecules provide this energy.
Below is the picture of the central dogma.
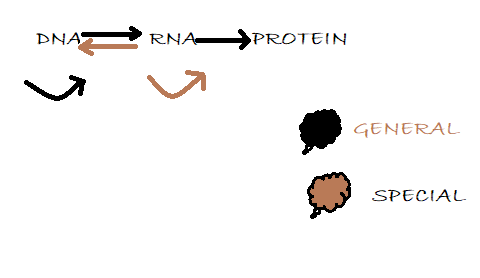
Note: The 'Core Dogma' is the method of translating the instructions in DNA into a functional product. Francis Crick, the discoverer of the structure of DNA, first suggested it in 1958. The core dogma explains the two-step mechanism of transcription and translation by which data flows into proteins in genes: DNA to RNA to protein.
