Question
Question: What is a sequential circuit?...
What is a sequential circuit?
Solution
Sequential logic, in automata theory, is a form of logic circuit whose output is determined not only by the current value of its input signals, but also by the sequence of previous inputs, or input history. The output of combinational logic, on the other hand, is a function of only the current input. Sequential logic, on the other hand, contains state (memory), but combinational logic does not.
Complete answer:
A sequential circuit is a combinational logic circuit that has inputs (X), logic gates (Computational circuit), and outputs (Y) (Z). A sequential circuit provides an output based on current input and past input variables, whereas a combinatorial circuit produces an output based on simply the input variable. That is to say, sequential circuits have memory components capable of storing binary data. The state of the sequential circuit at the time is defined by the binary information. A latch that can store only one bit of data.
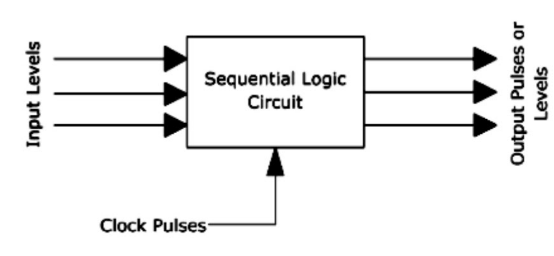
The Asynchronous sequential circuits do not need the clock signals. The asynchronous circuit is controlled by pulses. As a result, changes in the input might affect the circuit's state. Clock pulses are not used in asynchronous circuits. When the input variable is modified, the internal state is altered. The memory components of asynchronous sequential circuits are un-clocked flip-flops or time-delayed flip-flops. Asynchronous sequential circuits are comparable to feedback-based combinational circuits.
The clock signal synchronises the state of the memory element in synchronous sequential circuits. Flip-flops or latches are used to store the output (memory devices). The outputs are synchronised using either only the clock signal's negative edges or only the clock signal's positive edges.
Note:
There are two types of digital sequential logic circuits: synchronous and asynchronous. The state of the device in synchronous sequential circuits changes only at discrete moments in response to a clock signal. The state of the device in asynchronous circuits can change at any moment in response to changing inputs.
