Question
Question: What is a Monohybrid cross? What is its ratio? Show with the help of a checkerboard....
What is a Monohybrid cross? What is its ratio? Show with the help of a checkerboard.
Solution
Mendel is the father of genetics. He investigated a pair of pea plants with contrasting traits and studied seven characters with contrasting traits: flower colour, flower position, pod colour, pod shape, seed colour, seed shape and stem height.
Complete answer:
In a monohybrid cross, two homozygous plants for contrasting traits are crossed, this results in a heterozygous offspring. It is responsible for the inheritance of one gene and can be easily demonstrated by Punnet Square.
MONOHYBRID CROSS DEMONSTRATION
Let us carry out a monohybrid cross between a homozygous tall pea plant (TT) and a homozygous dwarf pea plant (tt)
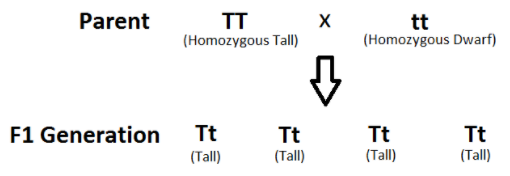
It was observed that all the pea plants in the F1 generation resemble one parent and the character of the other parent was lost i.e. all pea plants were tall with heterozygous genotype (Tt). Two plants from this generation were again crossed with each other and F2 generation was observed using a punnet square.
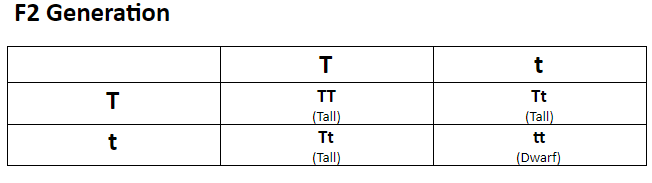
From the above checkerboard, we can see that when two plants from the F1 generation were crossed, four offspring were produced and the traits that were absent in the F1 generation reappeared in the F2 generation (in this case dwarf plant).
We can conclude-
PHENOTYPIC RATIO
Tall: Dwarf - 3:1
This means that 3 out of 4 plants were tall and only one was dwarf.
GENOTYPIC RATIO
TT:Tt:tt – 1:2:1
This means that one out of four plants were homozygous tall, two were heterozygous tall and one was a homozygous dwarf.
Note: Using this monohybrid cross Mendel proposed the Law of Dominance which says that out of the two contrasting traits one which appears in the F1 generation is dominant over the other. The trait which is absent in the F1 generation is called a recessive trait. In this case, tall stem height is a dominant trait and dwarf stem height is a recessive trait.
