Question
Question: What is a cytoskeleton?...
What is a cytoskeleton?
Solution
The following are some of the most important cytoskeleton functions: It gives the cell form and support. It aids in the development of vacuoles. It keeps the various cell organelles in place. It helps with cell signalling. It facilitates intracellular motions such as cell organelle migration and vesicle trafficking in and out of the cell.
Complete solution:-
All cells, including bacteria and archaea, have a cytoskeleton, which is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments found in their cytoplasm. It runs from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane in all organisms and is made up of identical proteins.
The cytoskeleton is a framework that helps cells maintain their shape and internal order, as well as providing mechanical support for cell division and movement.
The cytoskeleton is a network of fibres that makes up eukaryotic, prokaryotic, and archaean cells. Eukaryotic cells' fibres are made up of a complex web of protein filaments and motor proteins that aid cell movement.
It gives the cell structure and support, organises the organelles, and promotes molecular movement, cell division, and cell signalling.
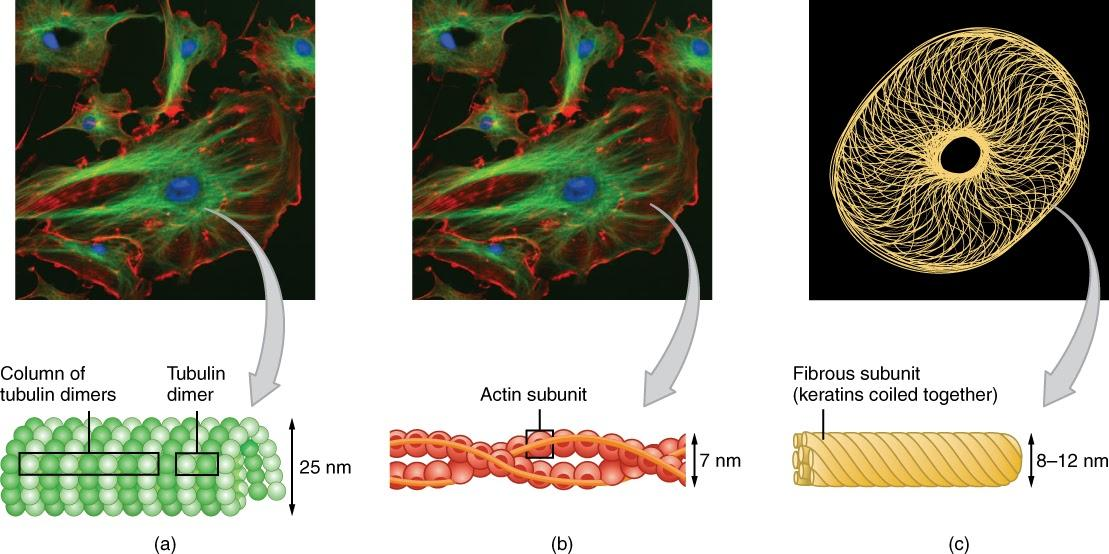
The following types of fibres make up a cytoskeleton structure:
Microfilaments
Microtubules
Intermediate Filaments
Microtubules are spherical, hollow tubes with a diameter of around 24 nanometers. Tubulin is a protein that makes them up. A single tubulin tube is made up of thirteen tubulins linked together. Microtubules are highly dynamic structures that exhibit their ability to change rapidly. They continue to grow or diminish at a steady rate. During cell division, they aid in the movement of cellular components and the division of chromosomes.
Microfilaments are thread-like protein fibres with diameters ranging from 3-6 nm. They're especially prevalent in muscle cells. They are made up of the actin protein, which is responsible for muscle contraction. Cellular motions such as cytokinesis, contraction, and gliding are also controlled by these proteins.
Intermediate Filaments
The intermediate filaments have a diameter of around 10 nm and provide the cell with tensile strength. Keratin and neurofilament production is aided by them.
Certain motor proteins are also found in the cytoskeleton. These are some of them:
Kinesin
These proteins travel along microtubules, which transport biological components. The organelles are dragged along the cell membrane by them.
Dyneins
The cell organelles are dragged towards the nucleus by them.
Myosin
These are responsible for muscular contractions via interacting with actin protein. Cytokinesis, exocytosis, and endocytosis are also performed by them.
Note:-
Eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells, and archaeans all have a cytoskeleton, which is a network of fibres that serves as their "infrastructure." These fibres in eukaryotic cells are made up of a complex web of protein filaments and motor proteins that help the cell move and stay stable.
