Question
Question: What is a Biuret test?...
What is a Biuret test?
Solution
Hint: Before attempting this question, one must have prior knowledge of oxidation and reduction, and how it leads to change in color, especially in the case of Cu2⊕ and ion.
Complete answer:
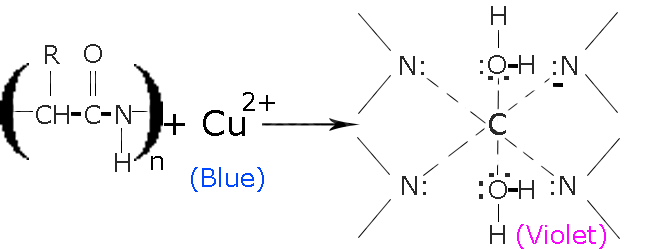
The Piotrowski’s test, or as it is more commonly known, Biuret test. This test is used, when we have to detect the presence of peptide bonds in an alkaline solution.
Interestingly, the biuret test does not use the reagent biuret. Instead, it uses a mixture of sodium hydroxide and hydrated Copper (II) SulfateCu⊕ as reagents. Potassium Sodium Tartrate is also used to stabilize the chelate formed.Cu2⊕
Reaction: In the presence ofNaOH, Cu2⊕ from hydrated Copper (II) Sulfate(CuSO4.xH2O) is released. Then combine with peptide molecules to form a chelate as shown below.
The reaction occurs in two steps:-
- Copper(II) binds with nitrogen, that are present in the protein’s peptide chains
- In the 2nd step Copper (II) is reduced to Copper (I), which gives the solution its iconic light-purple color.
The biuret solution is blue in color and turns light-purple, when it reacts with compounds containing peptide bonds.
The biuret can also be used to measure the concentration of proteins, by using the Beer-Lambert law i.e. the intensity of the color (absorption of light at 540nm) is directly proportional to the protein concentration
Note: Buffers, like Ammonia interfere with the reaction, therefore this test is not suitable for protein samples purified from ammonia sulfate precipitation. The NaOHsolution used should be concentrated and then followed by a few drops of hydrated Copper (II) Sulfate(CuSO4.xH2O).