Question
Question: What happens to the gravitational force between two objects as the bodies become farther apart from ...
What happens to the gravitational force between two objects as the bodies become farther apart from each other?
Solution
Let us first define gravity before moving on to the question. In mechanics, gravity, often known as gravitation, is the universal force of attraction that operates on all matter. Because it is the weakest force known in nature, it has no effect on the inner properties of ordinary matter.
Complete step by step answer:
The universal force of attraction is gravity. It's the way the Earth keeps you grounded. Gravitational attraction is a force that attracts all objects. Gravity is a ubiquitous phenomenon. This gravitational attraction is proportional to the square of the distance between their centres and is directly proportional to the masses of both objects. This means that the gravitational pull reduces as you move away from an item.
Let's take a closer look at this.
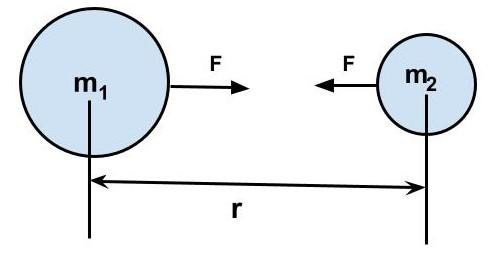 e
e
Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation has the following equation:
F=r2Gm1m2
As you can see, if Gm1m2 is constant, alternatively, if we say k=Gm1m2 , we can rewrite the equation as;
F=r2k
Or,
Fαr21
As a result, the force between the two bodies is inversely proportional to the square of their radius, and the gravitational attraction weakens as the distance between them grows.
Note: Gravity is the weakest of the four fundamental interactions in physics, with a strength of around 1038 times that of the strong interaction, 1036 times that of the electromagnetic force, and 1029 times that of the weak interaction. As a result, it has no discernible effect at the subatomic particle level. On the macroscopic scale, however, it is the main interaction that causes the formation, shape, and trajectory (orbit) of astronomical bodies.
