Question
Question: What does the \[{\text{N}}\] designation mean in organic chemistry? For example: \[{\text{N - hydrox...
What does the N designation mean in organic chemistry? For example: N - hydroxymethylurea?
Solution
Hint : N in chemistry is the atomic symbol of nitrogen. In organic chemistry, it is usually associated with amines and amides. So, try to look out for the IUPAC nomenclature of amines and amides while answering the question.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
N designation means that a substituent group is attached to a nitrogen atom (symbol N).
Since urea is an amide, it follows amine/amide naming conventions that specify when a substituent is bound onto nitrogen and not bound onto something else.
In the question, the name of the given example is written incorrectly. The correct way of writing the compound name is N - (hydroxymethyl)urea. Another name for N - (hydroxymethyl)urea is methyl urea. Here, the −ol conveys that there is an alcohol group that is attached to urea. Also, methyl emphasizes that it's not a −CH3OH (with no other bond on C), but a −CH2OH.
N - (hydroxymethyl)urea tells us that a −CH2OH group is attached on one of the nitrogen atoms in urea, H2N(C=O)NH2, in place of one of the hydrogens. The structureN - (hydroxymethyl)urea is as shown in the diagram below:
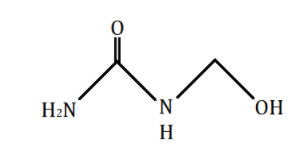
Additional Information:
Methylolurea is the product of the condensation reaction of formaldehyde and urea. It is an intermediate in fertilizer compositions. It also has the properties of a corrosion inhibitor.
Note :
Be careful about hydroxymethyl and do not confuse it with methoxy. Hydroxymethyl implies an alcohol substituent, but methoxy is an alkoxide (deprotonated alcohol) substituent. For the above compound, if you wrote, N,N′−dimethylurea, then it would have shown that the first nitrogen emphasized (N) is not the same as the second nitrogen emphasized (N′), and each singular methyl is on a different nitrogen.
