Question
Question: What does aromatization mean?...
What does aromatization mean?
Solution
Aromatic compounds are synthetic compounds that consist of formed planar ring frameworks joined by clouds of delocalized pi-electrons instead of individually exchanging double bonds and single bonds. We can also call aromatic compounds as aromatics (or) arenes. We know the toluene and benzene are examples of aromatic compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us now see what aromatization means?
We have to know that aromatization is a synthetic reaction where an aromatic compound is obtained from a single precursor that is non-aromatic. Normally aromatization is accomplished by dehydrogenation of existing cyclic mixtures, shown by the transformation of cyclohexane into benzene. Aromatization incorporates the development of heterocyclic compounds.
Let us now see an example of a compound that undergoes aromatization reaction.
We know that methylcyclohexane is a non-aromatic compound; we can turn it to aromatic benzene, by treating it with platinum and heating it. During this reaction, hydrogen gas is also evolved. We can write chemical equation for this aromatization reaction as,
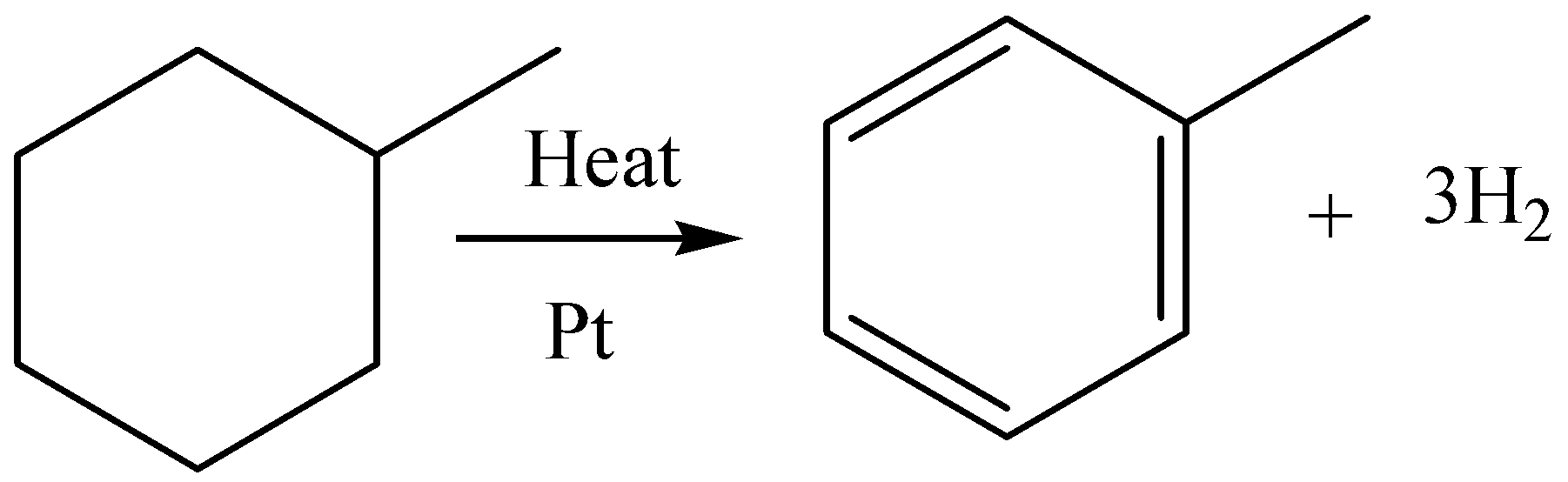
We have to know that there are four common methods of aromatization. They are,
- Dehydrogenation of naphthenes
- Hydroisomerization of naphthenes
- Dehydrocyclization of aliphatic hydrocarbons
- Condensation of hydrocarbons
Let us now define the four common methods of aromatization with examples.
Dehydrogenation of naphthenes: We have to know naphthenes are a class of cyclic aliphatic hydrocarbons obtained from oil. They have the overall equation CnH2n. The easiest naphthene is cyclohexane,C6H12. Benzene could be obtained by catalytic dehydrogenation of cyclohexane. We can write the equation as,
C6H12→C6H6+3H2
Hydroisomerization of naphthenes: We can obtain benzene by catalytic isomerization and dehydrogenation of methylcyclopentane. We can write the equation as,
C6H9CH3→C6H6+3H2
Dehydrocyclization of aliphatic hydrocarbons: We can obtain toluene by Dehydrocyclization of aliphatic hydrocarbons such as toluene. We can write the equation as,
C7H16→C6H5CH3+3H2
Condensation of hydrocarbons: At the time of cracking of petroleum, we can convert propane to benzene at 600−800∘C.
3C3H8→C6H6+3CH4+3H2
Note: Steroids are aromatized by enzymes known as aromatases. With the help of aromatases, testosterone could be converted to estradiol, and estrone could be obtained from androstenedione. Hydride and abstraction of protons is also an aromatization route. In the process of aromatization, sulfur and selenium are commonly used.
