Question
Chemistry Question on Environmental Chemistry
What causes poisoning of Carbon Monoxide?
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning occurs when an individual inhales or is exposed to high levels of carbon monoxide gas. Carbon monoxide is produced by the incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels such as gasoline, natural gas, wood, coal, and propane. It is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas, making it difficult to detect without specialized equipment.
The main cause of carbon monoxide poisoning is the inhalation of carbon monoxide gas. This gas binds to hemoglobin in red blood cells, forming carboxyhemoglobin. Carboxyhemoglobin has a much stronger affinity for oxygen than regular hemoglobin, which prevents the transport of oxygen to body tissues. As a result, oxygen deprivation occurs, leading to cellular damage and potentially life-threatening conditions.
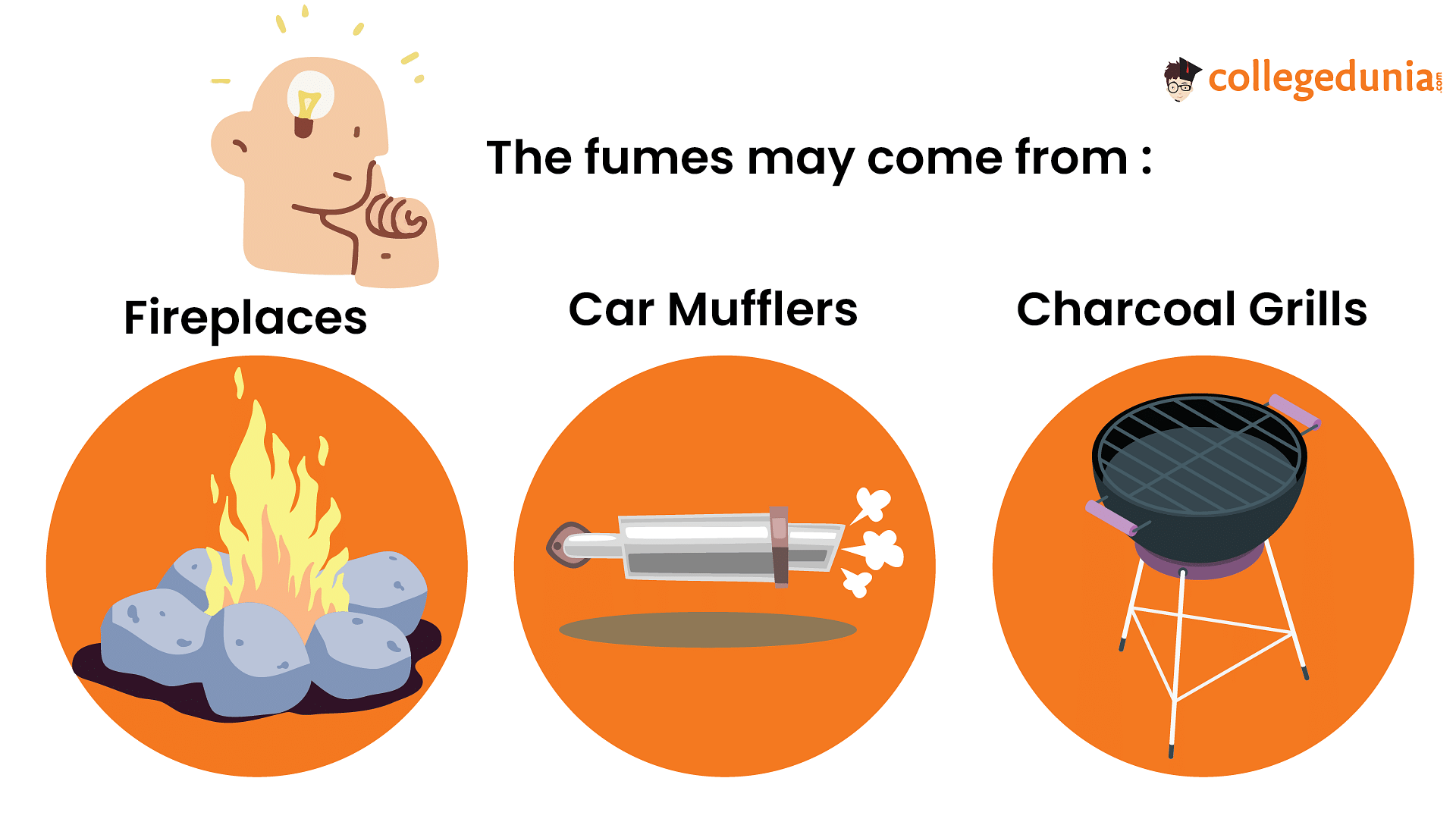
Common sources of carbon monoxide include:
- Faulty or poorly maintained fuel-burning appliances: This includes malfunctioning furnaces, gas stoves, water heaters, fireplaces, and space heaters.
- Vehicle exhaust: Carbon monoxide can accumulate in enclosed spaces such as garages, tunnels, or poorly ventilated areas near running vehicles.
- Generators and power tools: Operating gasoline-powered generators or tools in enclosed spaces without proper ventilation can lead to carbon monoxide buildup.
- Tobacco smoke: Smoking or inhaling secondhand smoke exposes individuals to carbon monoxide, which can contribute to overall carbon monoxide levels in the body.
- Blocked chimneys or vents: Blockages in chimneys, flues, or vents can cause carbon monoxide to back up into living spaces instead of being properly vented outdoors.
The symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning can vary depending on the level and duration of exposure. Early symptoms often resemble flu-like symptoms, including headaches, dizziness, nausea, fatigue, and confusion. Prolonged exposure to high levels of carbon monoxide can lead to loss of consciousness, seizures, organ damage, and even death.
To prevent carbon monoxide poisoning, it is crucial to have fuel-burning appliances and heating systems inspected and maintained regularly. Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home, especially near sleeping areas. Ensure proper ventilation and avoid running vehicles or gas-powered equipment in enclosed or poorly ventilated spaces. It is important to take immediate action and seek fresh air if you suspect carbon monoxide poisoning and to seek medical attention promptly.
