Question
Question: What are the types of intermolecular forces acting in the liquid state of krypton? What are the ones...
What are the types of intermolecular forces acting in the liquid state of krypton? What are the ones acting in the liquid state of nitrogen fluoride?
Solution
Hint : First determine the geometrical shape of krypton and nitrogen to check for polarity and nonpolarity of them. If the element or compound is non-polar then only London dispersion force is available. On the other hand, if the element or compound is polar, then along with London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole force will be available.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Krypton is a monatomic element, meaning that it can remain stable as a single atom. The monoatomic nature of krypton results in symmetrical geometry as the charges are distributed equally all over the atom. This symmetry makes krypton a non-polar element. We know that if an element or compound is nonpolar than London dispersion forces are the only intermolecular forces present in them.
Hence, London dispersion forces are the only intermolecular forces available in the liquid state of Krypton.
On the other hand, nitrogen fluoride has a geometrical shape of trigonal pyramidal. Due to this, the molecule of NF3 becomes polar. Also, if we check the Lewis dot structure of NF3 shown below, we can see that there is a lone pair available around the nitrogen atom as well as the three bonds it has with fluorine.
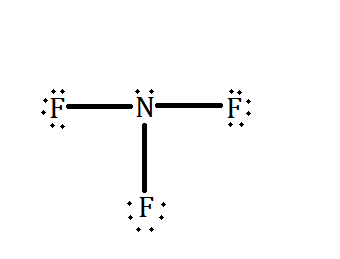
Since, the electronegativity of fluorine is higher than nitrogen and therefore, the lone pair of nitrogen is opposed by fluorine. This results in a partial negative charge at fluorine end and a partial positive charge at nitrogen end. Thus, creating a dipole – dipole force among them.
Hence, in the liquid state of nitrogen fluoride, dipole-dipole forces and London dispersion forces are available.
Note :
To determine whether the element is polar or nonpolar simply check the geometry of that element or compound. If one side of the compound is positive and the other side is negative then it will be a polar compound. If the charge is not concentrated on any one end and is distributed equally all over the compound, then it is a non-polar element.
