Question
Question: What are the total number of stereoisomers of \( 2,3 - \) dichlorobutane?...
What are the total number of stereoisomers of 2,3− dichlorobutane?
Solution
Isomerism is the property of chemical compounds in which compounds can exist in two different forms but having the same molecular formula. Stereochemistry is a type of isomer in which the position of substituents changes in three-dimensional orientation.
Complete answer:
Stereoisomerism of particular compounds have the same chemical formula, same number of atoms but only spatial arrangements differ. Therefore, stereoisomerism is also known as spatial isomerism.
2,3− dichlorobutane molecule do not give any geometric isomers because geometric isomerism is shown by the compounds having double bonds.
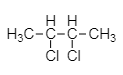
As we see, the 2,3− dichlorobutane molecule is symmetrical in nature due to the presence of the same substituent in the end.
2,3− dichlorobutane molecule has a two chiral center hence capable of rotating plane polarized light into right and left direction.
The mathematical formula which is used to calculate the total number of stereoisomers for an even number of chiral centers is;
S=2n−1+2n/2−1
Where S= total number of stereoisomers
n= Total number of chiral centers present in a molecule
As we noticed from the structure there are two chiral centers so the value of (n) is 2 .
Now put the value of (n) in the above formula-
S=22−1+222−1
After solving this equation, we get
S=21+20
S=2+1
Hence, the value of S after calculation is 3 .
Hence according to the formula there are a total of three stereoisomers possible for 2,3− dichlorobutane.
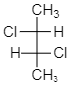
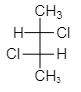
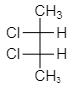
As we see from the above structure, figure (III) shows the presence of symmetry of a molecule and hence it is mesomeres. As we know mesomeres have net zero optical rotation therefore they are considered as an optically inactive isomer.
Hence the total number of stereoisomers of 2,3− dichlorobutane is 3 .
Note:
Enantiomers or optical isomers are two forms of stereoisomers which are mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable in nature. Diastereomers are two forms of stereoisomers which are non-mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable in nature.
