Question
Question: What are the structure of RNA and DNA and how one might be used to create the other?...
What are the structure of RNA and DNA and how one might be used to create the other?
Solution
Before studying the structures of DNA and RNA we must have a brief idea about what they are. They are the two main types of nucleic acids and both are made from nucleotides. DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid and RNA stands for Ribonucleic acid. DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell and also present in the mitochondria called as the mitochondrial DNA. RNA can be found freely in the cytoplasm, nucleus and sometimes in the ribosome.
Complete answer:
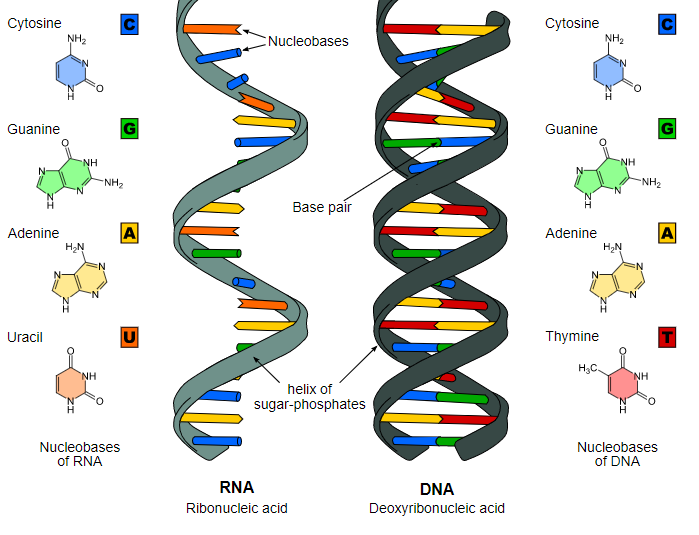
Firstly, the structure of DNA and RNA can be compared on the basis of their structures easily.
DNA is a long chain of polymer which contains deoxyribose and phosphate as a backbone. It is made from 4 different nucleotide bases where there are two purines and two pyrimidines. The purines are adenine[A] and guanine[G]. The pyrimidines are thymine[T] and cytosine [C]. The purines pair with pyrimidine. In this case adenine only pairs with thymine with double bonds present and cytosine pairs with guanine with triple bonds.
When we talk about RNA it is a polymer with ribose and phosphate backbone. Even RNA comprises 4 different bases but in this case, thymine is not present. In place of thymine uracil[U] is present and adenine pairs with uracil in RNA.
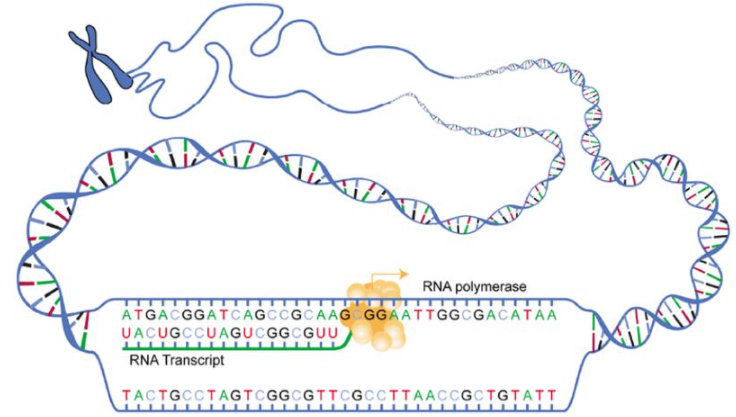
As now we are familiar with the structure of RNA and DNA, we can further study how DNA can be used as a template to make RNA. This process is called transcription which transfers the cell's genetic information from DNA to RNA. In this process the RNA copy is made from the genes DNA sequence.
The main enzyme responsible in transcription is RNA polymerase. It uses one single strand of DNA template to synthesize the complementary strand of messenger RNA. The site where RNA polymerase binds to the DNA template is called the promoter region, this region is found in the beginning of a gene. After binding the RNA polymerase opens the template strand. Then according to the DNA base pair one at a time complementary messenger RNA strands are produced. After the transcription is complete the messenger RNA strand undergoes translation.
The base pairings are:
Where DNA has T, complementary strand will have A; where DNA has A complementary will have U; when DNA has C complementary has G. Therefore, the RNA has the same information as the non-template strand of DNA. The only difference is that thymine is replaced by uracil.
Note: When we are studying about DNA, we must know that there are three different types of DNA. The different forms are A-DNA, B-DNA and Z -DNA. Where A and B are right-handed but Z- DNA is left handed. Like DNA even RNA is of three types all performing different functions. They are messenger RNA as seen in transcription, transfer RNA and ribosomal RNA.
