Question
Question: What are the possible isomers for \({C_3}{H_7}NO\)?...
What are the possible isomers for C3H7NO?
Solution
We can say that a molecule could contain a specific shape in space which could contribute to its nature. We have to know that isomers are molecules that are an indistinguishable number of atoms of each element yet several arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is the presence or plausibility of isomers.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to know that structural isomers of the compounds exhibit the same molecular formula but vary in the spatial arrangement of atoms and the state is called structural isomerism. Based on IUPAC naming, we could call structural isomerism as constitutional isomerism.
We can group structural isomers into three kinds,
- Chain isomers: The atoms of carbon are arranged in several sequences.
- Position isomers: The skeletal carbon chain remains unchanged, but the location of the functional group is varied. This classification of structural isomers is known as position isomers and the isomerism is called positional isomerism.
- Example: Compounds that have a molecular formula C3H7Br would be 1-bromopropane and 2-bromopropane. We can draw as,
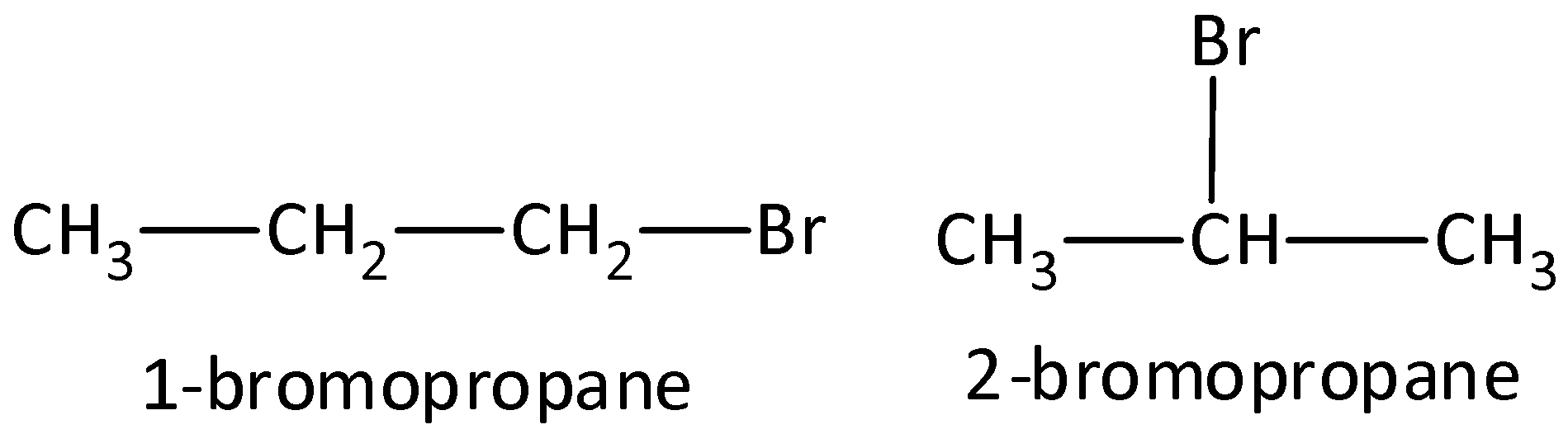
- Functional group isomers: The arrangement of atoms to make several various functional groups is known as functional group isomers and this is known as functional group isomerism. Example: Compounds that have a molecular formula C3H6O would be propanal (aldehyde) or a propanone (ketone). We can draw the structure as,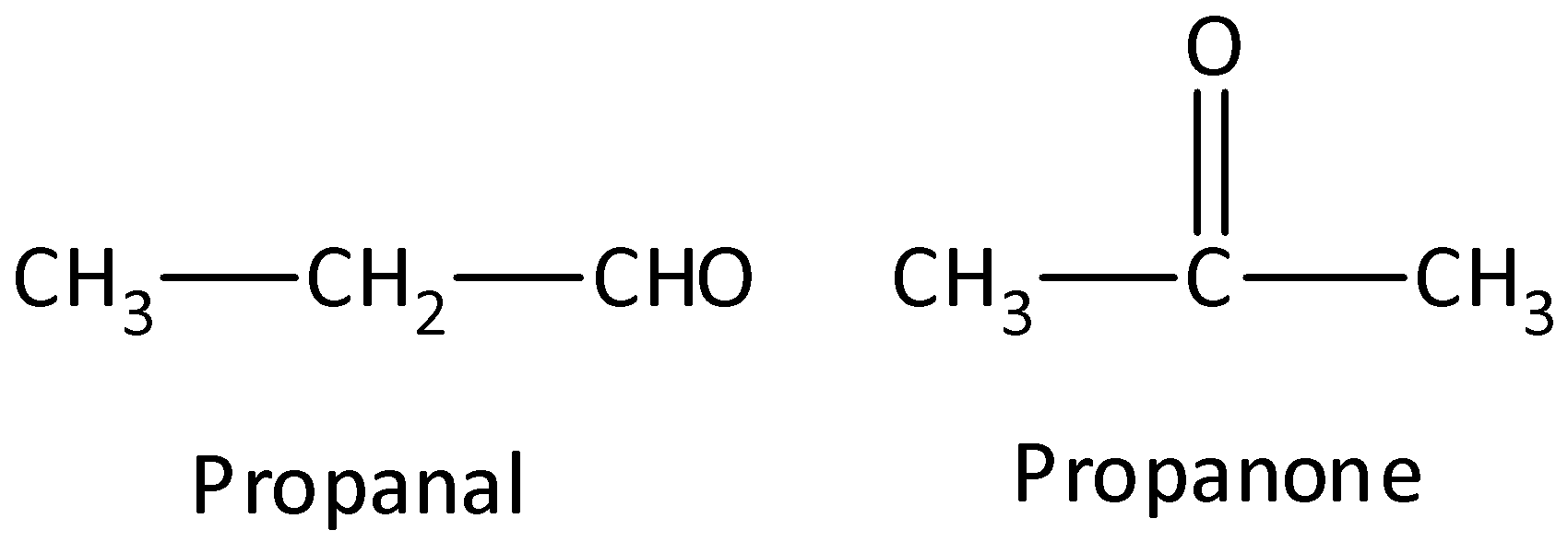
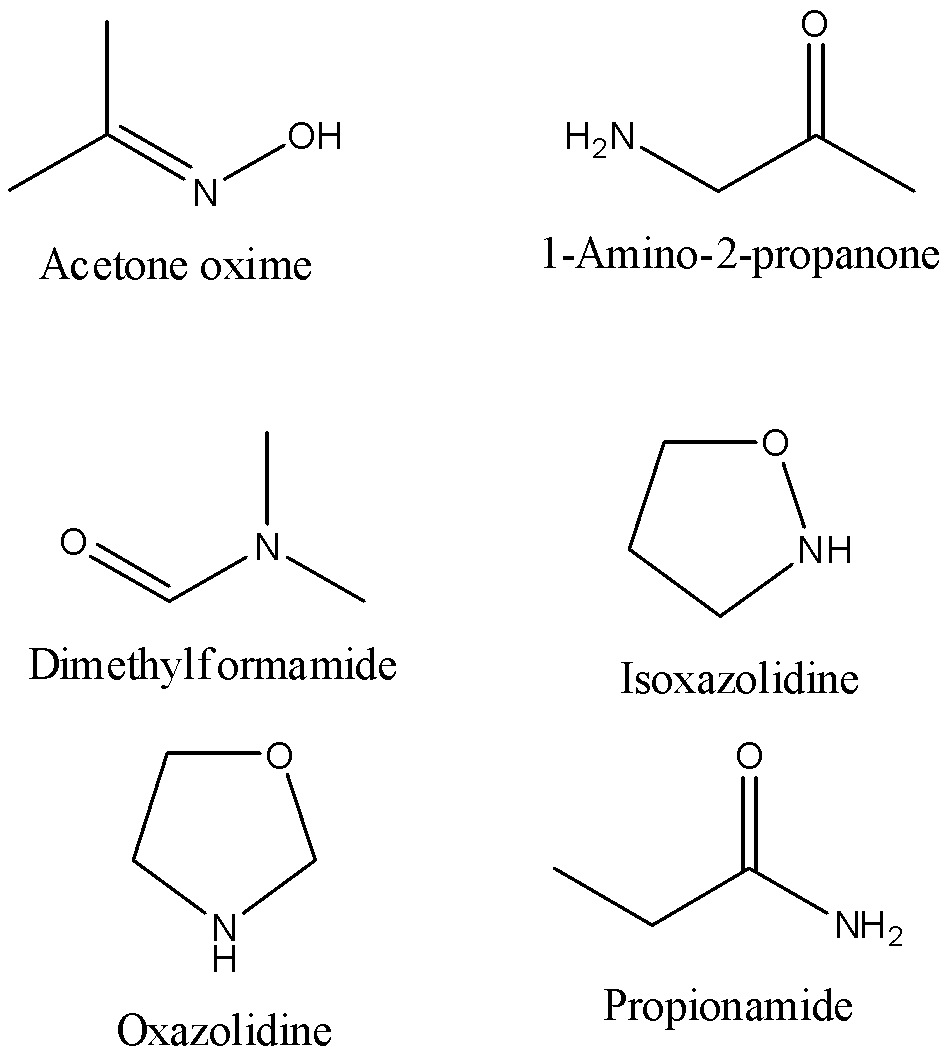
The possible isomers of C3H7NO are,
- Acetone oxime
- 1-Amino-2-propanone
- Dimethylformamide
- Isoxazolidine
- Oxazolidine
- Propionamide
We can draw the structure of these isomers as,
Note: We can say that structural isomers exhibit different chemical properties like lower melting and boiling points etc. We can say examples of stereoisomers as cis 2-butene and trans 2-butene. We can say examples of chain isomers as n-pentane, isopentane and neopentane.
