Question
Question: What are the geometrical isomers of 2-hexene?...
What are the geometrical isomers of 2-hexene?
Solution
We have to know that the geometrical isomers are compound species with similar sort and amount of ions as another species, yet having an alternate mathematical construction. Molecules or gatherings display distinctive spatial plans on one or the other side of a substance bond or ring structure and trans, signifying "on the opposite side".
Complete step by step answer:
We can see, there are two types of geometrical isomers of 2-hexene. They are cis-hex-2-ene and trnas-hex-2-ene.
We have to know the structure of cis-hex-2-ene. That has to be drawn below.
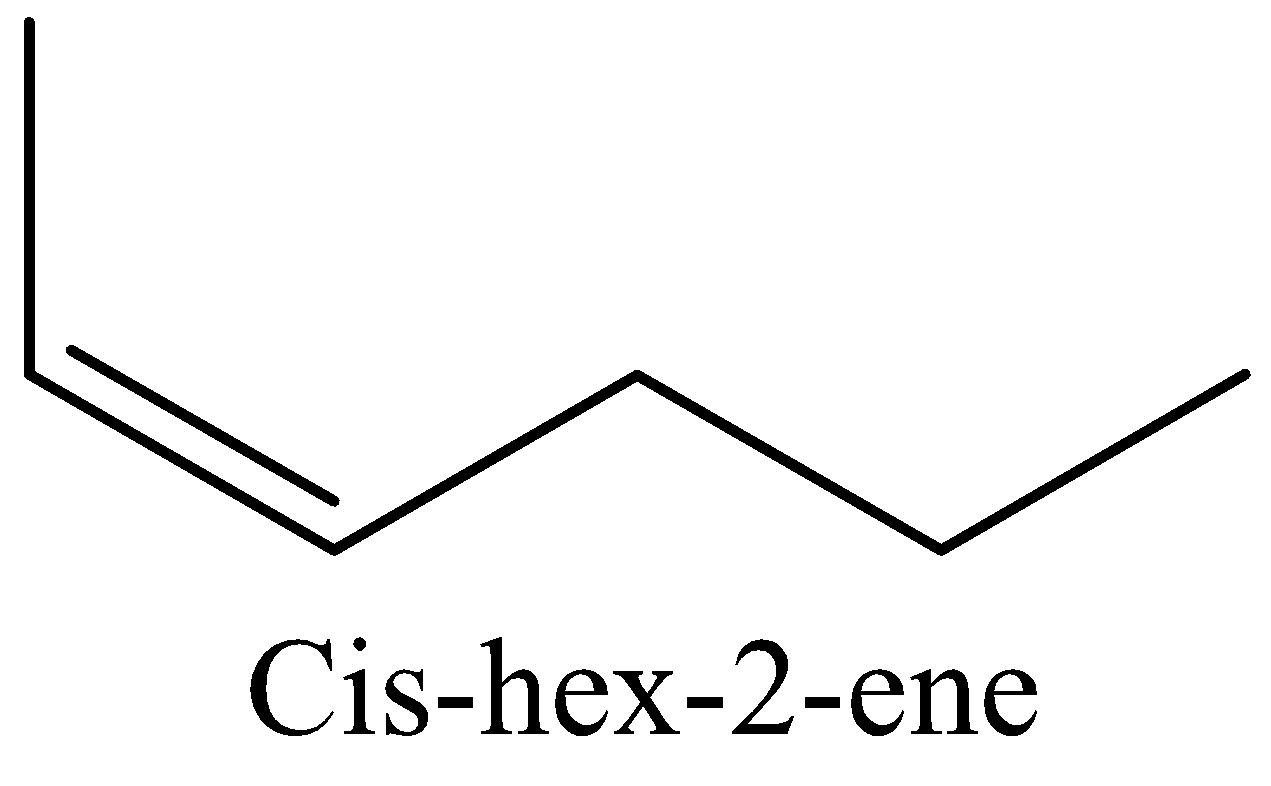
In this above cis-hex-2-ene structure, double bond placed in second carbon. Total number of carbons are present in the cis-hex-2-ene is six.
We have to know the structure of trans-hex-2-ene. That has to be drawn below.
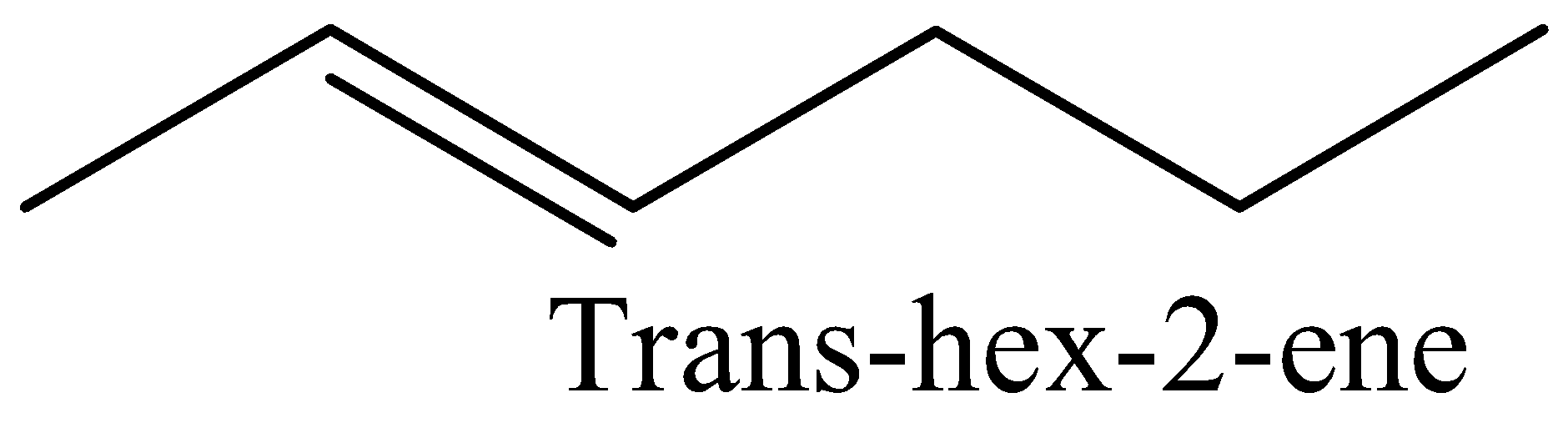
In this above trans-hex-2-ene structure, double bonds are placed in the second carbon. Total number of carbons present in the trans-hex-2-ene is six.
The dipole snapshot of cis-compound is an amount of the dipole snapshots of CCH3, and CCH2CH2CH3 bonds acting a similar way. The higher the extremity, the more prominent is the intermolecular dipole-dipole collaboration and the higher will be the limit.
Where, 1C can be cis or trans regarding as 4C . Presently these isomers have the same network. However, they are extraordinary geometry and they are in this way geometrical isomers. They would vary somewhat in bubbling, and softening point, and contrast all the more notably in their synthetic reactivity.
Note: We need to remember at the point when two mixtures have a similar subatomic equation and a similar underlying recipe however contrast in the spatial course of action of ions or gathering of particles because of the confined revolution of twofold bonds (about single bond on account of cyclic mixtures), they are said to display geometrical isomerism.
