Question
Question: What are the four processes of a Rankin cycle?...
What are the four processes of a Rankin cycle?
Solution
Hint : A Rankin cycle is a thermodynamic cycle very similar to the Carnot cycle in which a gas undergoes consecutive compressions and expansions at different conditions. In the Carnot cycle we deal with pressure-volume curves but in the Rankine cycle we deal with temperature-entropy curves.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Rankin cycle is a thermodynamic cycle describing the processes being carried out in various heat engines and steam turbines where the working fluid is reused and follows a closed loop. The ability of steam engines to transform thermal energies derived from fuels into electrical energy can be explained on the basis of four important cyclic processes that can be written as follows:
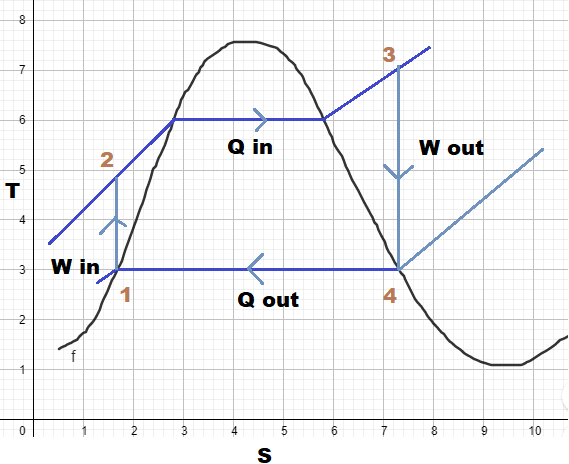
An isentropic compression (entropy constant): which involves pumping the working fluid (which is a liquid) from a low to high pressure by the aid of a little energy input.
An isobaric heat addition (pressure constant): which involves heating the high-pressure liquid inside the boiler at a constant pressure. This results in the formation of dry-saturated vapour
An isentropic expansion (entropy constant): which involves reducing the temperature and pressure of the dry-saturated vapour and allowing it to expand with the help of turbines. This process is accompanied by some condensation.
An isobaric heat release (pressure constant): which involves the condensation process that converts wet vapour into a saturated liquid with simultaneous heat rejection.
The T−S diagram can be represented as follows:
Note :
The limited efficiency of the Rankin cycle is attributed to the high heat of vaporization associated with the working fluid. The working temperature range of this cycle can be widened only under drastic conditions like super critical levels.
