Question
Question: What are \[SN1\] and \[SN2\] reactions? A) Addition Reaction B) Substitution Reaction C) Elimi...
What are SN1 and SN2 reactions?
A) Addition Reaction
B) Substitution Reaction
C) Elimination Reaction
D) Photochemical Reaction
Solution
It is easy to get this answer solved by looking at the questions and the given options. As the name says SN answer lies within it. 1 and 2 is used to define the order of the reaction and also to give the stability order for a particular reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
We are going to study about SN1 and SN2 reactions.
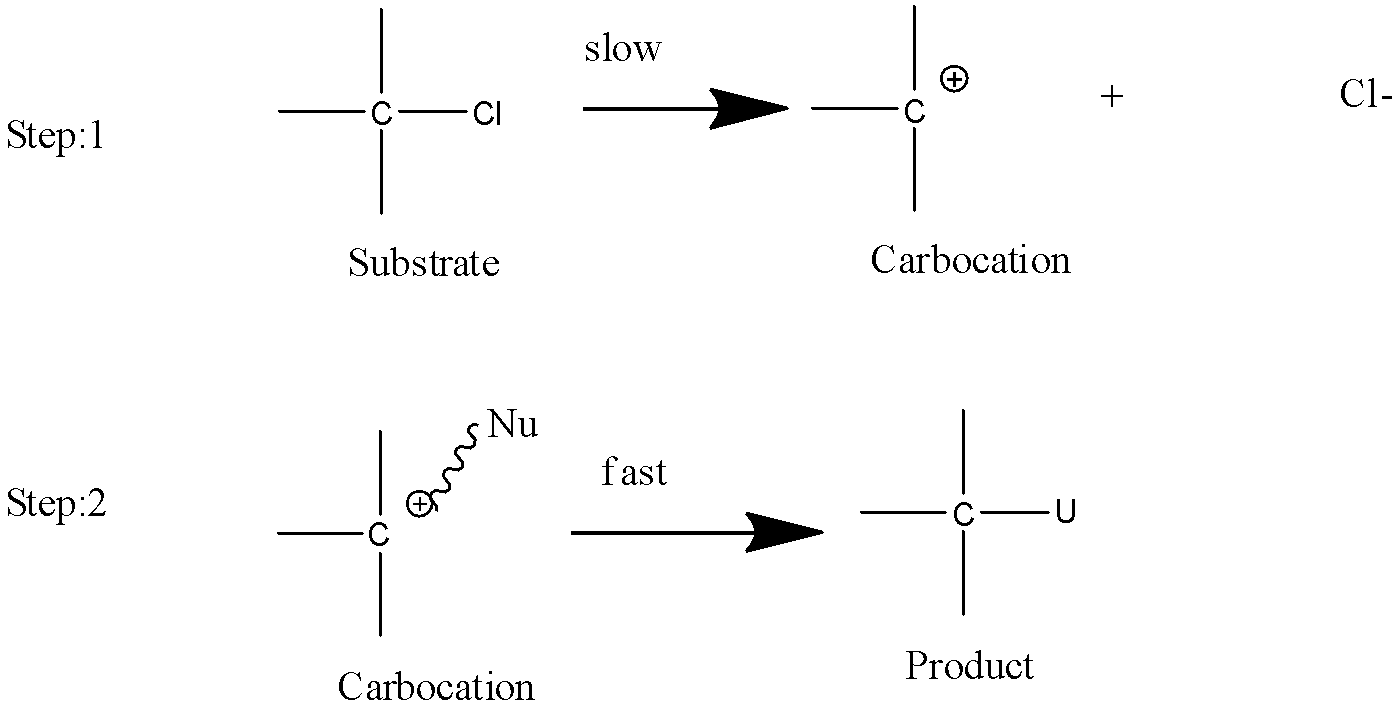
- SN1 reaction:
- It is a substitution reaction as the name says SN it means nucleophilic substitution reaction and 1 defines the rate determining step which is unimolecular in this type of reaction.
- The intermediate form in this type of reaction is carbocation due to which the stability order is 3∘>2∘>1∘.
- It is a first order reaction.
- SN2 reaction:
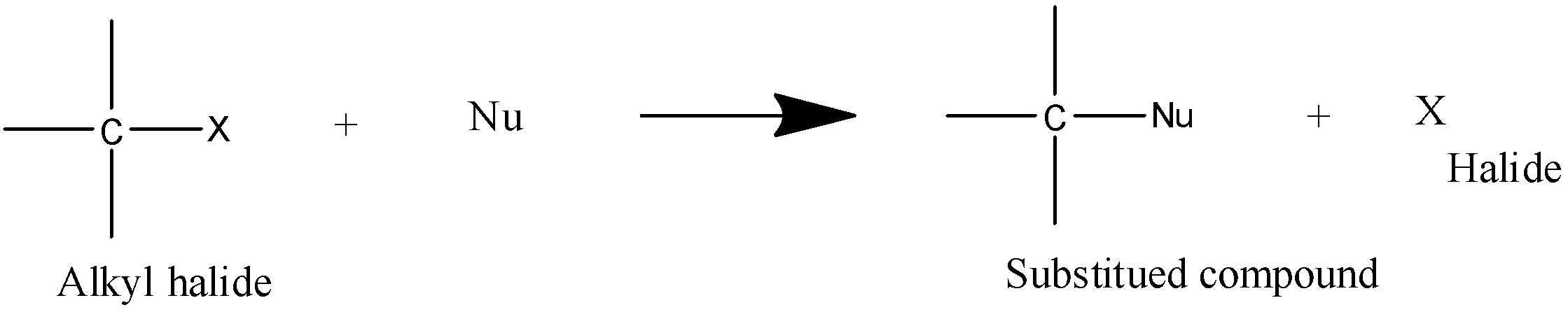
- It is a substitution reaction as the name says SN it means nucleophilic substitution reaction and 2 defines the rate determining step which is bimolecular in this type of reaction.
- Transition state is formed in SN2 reaction.
- Stability order is 1∘>2∘>3∘.
- It is a second order reaction.
Option A) this is an incorrect option since addition reactions are the one which involves the addition of two reactants or species.
Option B) This is a correct option since SN1 and SN2 are substitution reactions as explained above.
Option C) this is an incorrect option since Elimination reactions are the one in which substituents are removed from the molecule, but in SN1 and SN2 belongs to substitution type.
Option D) this is an incorrect option as photochemical reactions involve light at different frequencies.
Hence, the correct answer is, ‘Option B’.
Note: SN1 and SN2 are nucleophilic substitution reactions involving intermediates and transition states in them. The stability of the reaction depends upon the respective intermediates and transition states which is further easy to define the order of the reaction.
