Question
Question: What are reducing sugars?...
What are reducing sugars?
Solution
Let us get some ideas about reducing sugar. Any sugar that can operate as a reducing agent is referred to as a reducing sugar. A reducing sugar forms an ald
ehyde or ketone in an alkaline solution, allowing it to act as a reducing agent, as in Benedict's reaction. The sugar becomes a carboxylic acid as a result of this reaction.
Complete answer:
All monosaccharides, as well as some disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides, are reducing sugars. The aldoses, which have an aldehyde group, and the ketoses, which have a ketone group, are the two types of monosaccharides. Before ketoses may operate as reducing sugars, they must first tautomerize to aldoses. Galactose, glucose, and fructose, all prevalent dietary monosaccharides, are all reducing sugars.
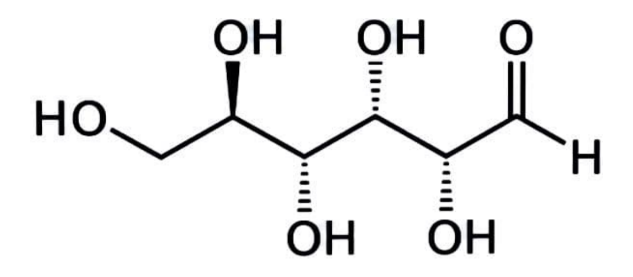
Disaccharides are made up of two monosaccharides and are either reducing or nonreducing in nature. Non Reducing disaccharides, such as sucrose and trehalose, have glycosidic linkages between their anomeric carbons, preventing them from converting to an open-chain form with an aldehyde group. Only one of the two anomeric carbons in reducing disaccharides like lactose and maltose is involved in the glycosidic bond, while the other is free and can convert to an open-chain form with an aldehyde group.
Note:
The Maillard reaction, which occurs when food is cooked at high temperatures and is crucial in defining food flavour, involves reducing sugars reacting with amino acids. In addition, the amount of reducing sugars in wine, juice, and sugarcane is a good indicator of the product's quality.
