Question
Question: What are Étard Reaction and Gattermann Koch Reaction? Give one example of each....
What are Étard Reaction and Gattermann Koch Reaction? Give one example of each.
Solution
In Etard Reaction, we carry out oxidation using chromyl chloride. It involves direct oxidation. In the Gattermann – Koch reaction, aromatic compounds are formulated using a Lewis acid.
Complete step by step solution:
Etard Reaction is named after the French chemist Alexandre Léon Étard and the Gattermann – Koch reaction is named after the two German chemists Ludwig Gattermann and Julius Arnold Koch. First let us discuss the Etard reaction.
Étard Reaction: At first chromyl chloride, which is a weak oxidizing agent, reacts with toluene in presence of non-polar solvent carbon tetrachloride. This leads to homolytic cleavage of bonds of chromyl chloride. In the similar manner, Étard complex is formed through the homolytic cleavage of C-H bonds of methyl group. Finally, the two molecules of Cr(OH)2Cl2 are removed through hydrolysis of the Étard complex and hence, the formation of benzaldehyde (aldehyde). Étard Reaction offers a way to oxidize aromatic methyl groups.
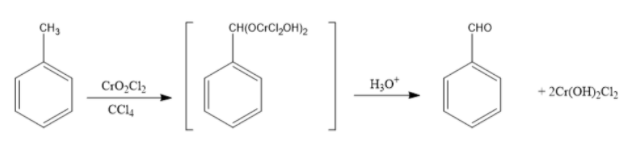
Now, let us discuss the Gattermann-Koch reaction.
Gattermann–Koch reaction: The Gattermann-Koch Reaction gives the mechanism of formation of an aryl aldehyde with the help of carbon monoxide and hydrochloric acid as reactants. Aluminum trichloride acts as a catalyst in the presence of trace amounts of cuprous chloride. We can take an example where benzene is converted into benzaldehyde. Now, let us see the mechanism- First carbon monoxide reacts with HCl and forms formyl chloride.
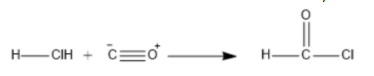
Then the formyl chloride reacts with anhydrous aluminum chloride and forms an electrophile H−C⊕=O .

Finally, H−C⊕=O reacts with benzene and forms benzaldehyde. During the reaction in this step AlCl3 and HCl is removed.
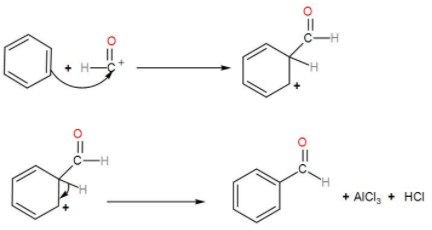
We can see the mechanism of the given reactions in the above discussion and that is the required answer.
Note: We should not be confused between Gattermann and Gattermann – Koch reaction. The Gattermann reaction uses a mixture of hydrogen cyanide and hydrochloric acid and Gattermann-Koch uses carbon monoxide instead of hydrogen cyanide. This is also a method of preparation of aromatic aldehydes like benzaldehyde salicylaldehyde etc. In this reaction benzene or phenols are treated with H-CN and HCl in presence of AlCl3.
