Question
Question: What are cycloalkanes?...
What are cycloalkanes?
Solution
Hint : Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that consist of chains of carbons and hydrogen atoms attached to carbon atoms, all bonded by single sigma bonds. Cycloalkanes are single closed ring compounds, which are similar to alkanes, all carbon is connected with single bonds in such a way that it gives a closed structure.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Alkanes are organic compounds formed by covalent bonds of only carbon and hydrogen (also known as hydrocarbon). Alkanes contain either a straight or branched chain of carbon, and hydrogen attached to all carbons as per the requirement of carbon i.e. form for covalent bonds.
In alkanes, all carbons are connected by a single sigma bond only. The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n+2 , where n is the number of carbons.
Now, for a straight carbon chain, if one hydrogen atom is removed from each carbon on both ends of the chain, both carbon will be one electron-deficient and need to make a covalent bond to be stable.
Hence, if the chain is bent and the carbon at both ends is bonded with each other, a cyclic structure will be formed, which still has the same structure like alkanes, where all carbon are bonded with each other by a single covalent bond, but with two fewer hydrogen atoms.
These compounds are known as cycloalkanes. The general chemical formula for cycloalkanes will have two fewer hydrogen atoms i.e. CnH2n
The nomenclature of cycloalkanes is similar to alkanes, with the only addition of the prefix to the name of the carbon chain.
Let us consider propane as an example whose structural formula is given as
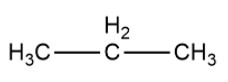
Now, we will remove hydrogen atoms from carbon on both ends
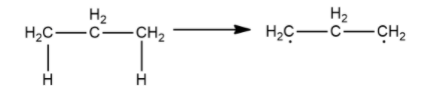
As both carbons have a lone electron and need to make a covalent bond to become stable, they will bond with each other as shown
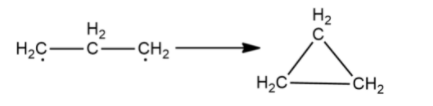
The final product is known as cyclopropane. Similarly, cycloalkanes can be obtained from alkanes for a carbon chain of greater than or equal to three carbons.
Note :
Here, we must know to differ between aromatic compounds and cycloalkanes. Even though both possess a cyclic closed structure, they are very different from each other. Aromatic compounds contain a hexa-carbon compound connected by alternate double bonds, which we also known as Benzene. Cycloalkanes are saturated compounds, in which all the carbons will be connected by single sigma bonds only.
